
What is Colocation Hosting? A Beginner’s Guide
Contributors IT Web Hosting Tips Updated on : January 28, 2026Colocation is mainly utilized if you work in web hosting. Many IT organizations use this service to quickly set up computing resources. It states that a third-party data center can offer you server rack space and all the necessary equipment, such as a power supply and cooling system.
Table of Content
Traditional data centers also have limited functionality and inadequate ventilation. Independent cooling and power backup systems are standard in modern data centers, and most have unique features to prevent computer overheating. This article will explore colocation hosting and how it can help you transform your business.
What is Colocation Hosting?
Colocation hosting, or “colo,” refers to renting space in a third-party data center. Businesses can also easily purchase server space at colocation data centers and benefit from enhanced security and uptime guarantees.
Also, most organizations store their vital equipment in colocation facilities as they do not operate or own data centers. For instance, you have a robust computer that runs your websites and business apps. Still, you need a safe and secure place with good internet connectivity and reliable power to store it.
Therefore, in colocation hosting, you pay to place your server in a proficient data center that offers everything required, such as security, electricity, cooling, and a high-speed internet connection. You still own and maintain the server, but the data center keeps running smoothly. Now, let’s understand how Colocation hosting works.
Key Aspects of Colocation Hosting
1. Physical Space
Businesses rent space in a third-party data center to house their servers. This can range from a single rack unit to a full cabinet or even a private cage.
2. Infrastructure
The colocation provider supplies critical infrastructure such as power, cooling systems, high-speed internet connectivity, physical security, and backup systems to ensure uptime and reliability.
3. Ownership
Unlike traditional hosting, the client owns and maintains the server hardware, storage, and software. The provider only offers the facility and supporting resources.
4. Control
Organizations retain complete administrative and operational control over their servers, including configurations, upgrades, and maintenance, while leveraging the data center’s environment.
5. Cost
Colocation reduces expenses compared to building and maintaining a private data center. Costs mainly include renting rack space, bandwidth, power consumption, and support services.
How Does Colocation Hosting Work?
– Colo hosting facilities provide clients with complete server space, physical infrastructure, and security. Clients can also set up their servers in a reserved cage, rack, or other space.
– Reputable colocation server hosting also utilizes a pay-per-KWH business model that helps organizations optimize the power and infrastructure of a data center at a lower initial cost. Organizations save money under this approach as they only pay for the resources they utilize.
– Organizations shifting to a colocation center must confirm sufficient power equipment, uplink posts, IP addresses, and server rack space. It is best to review their evaluations and suggestions to learn more about the service provider and ensure which trustworthy option they provide.
Types of Colocation Data Center Facilities
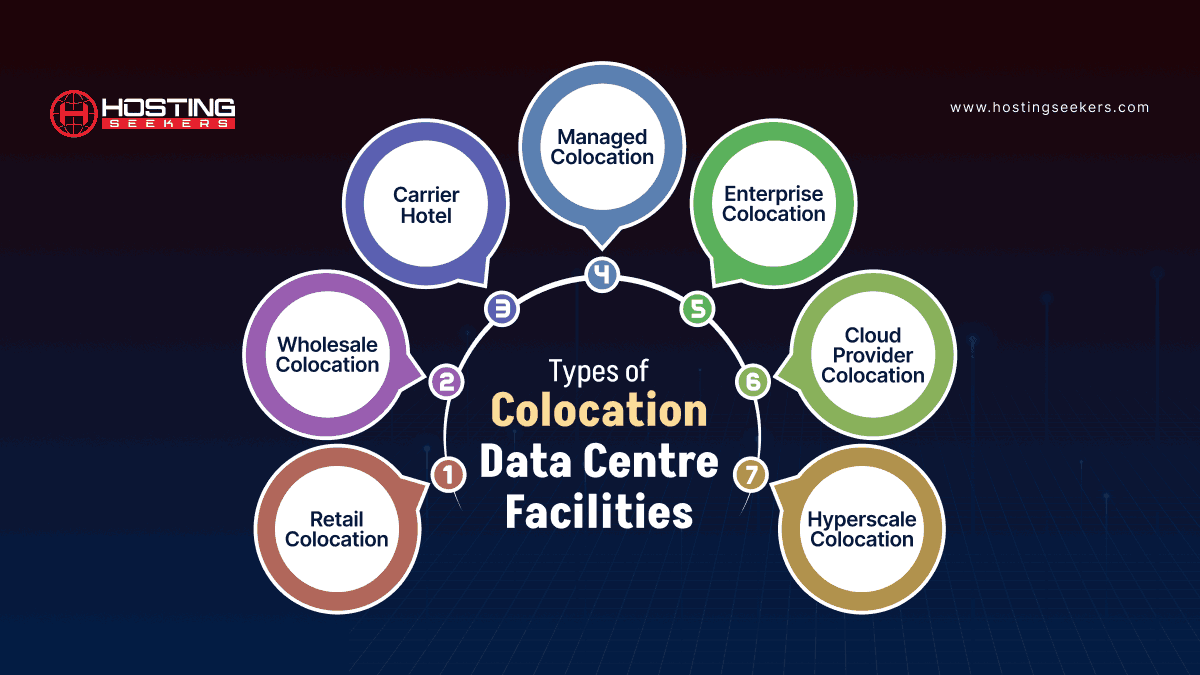
Colocation data center facilities come in different types, each offering different requirements and scales of operations. Here are the main types:
1. Retail Colocation
This facility provides space in small units like cages or racks. It is good for small–to medium-sized businesses that require a limited amount of space and prefer the data center to handle infrastructure management and maintenance.
2. Wholesale Colocation
This type offers larger spaces, mostly complete rooms, suites, or floors. It is suitable for large enterprises or companies with substantial IT infrastructure needs, providing more control over the space and sometimes infrastructure.
3. Cloud Colocation
Cloud colocation is when businesses place their servers and IT hardware inside a third-party data center that is specifically designed to support cloud computing environments.
Instead of running servers on-site, companies rent physical space (racks, cages, or suites) in a colocation facility. They connect this infrastructure directly to public, private, or hybrid cloud platforms (like AWS, Azure, Google Cloud).
4. Edge Colocation
Edge colocation places servers and networking equipment in smaller, localized data centers that are close to end users or devices (the “edge” of the network). Instead of relying on a centralized data center far away, businesses use regional colocation facilities near users. This reduces the distance data must travel, improving latency and performance.
3. Carrier Hotel
A facility that offers interconnection points for multiple telecommunication carriers and other network providers. It serves as a good hub for data exchange and connectivity.
4. Managed Colocation
In addition to offering space and power, managed colocation facilities provide different managed services, such as security, monitoring, hardware maintenance, and networks.
5. Enterprise Colocation
Mainly developed and designed for large businesses, these facilities offer customizable space and higher levels of security and control to meet the unique needs of enterprise clients.
6. Cloud Provider Colocation
These data centers are optimized for cloud service providers, providing scalable infrastructure and connectivity to support cloud operations.
7. Hyperscale Colocation
Tailored for hyperscale clients like major tech companies with massive data requirements, these facilities offer extensive space, power, and cooling infrastructure to support large-scale deployments.
Benefits of Colocation Hosting
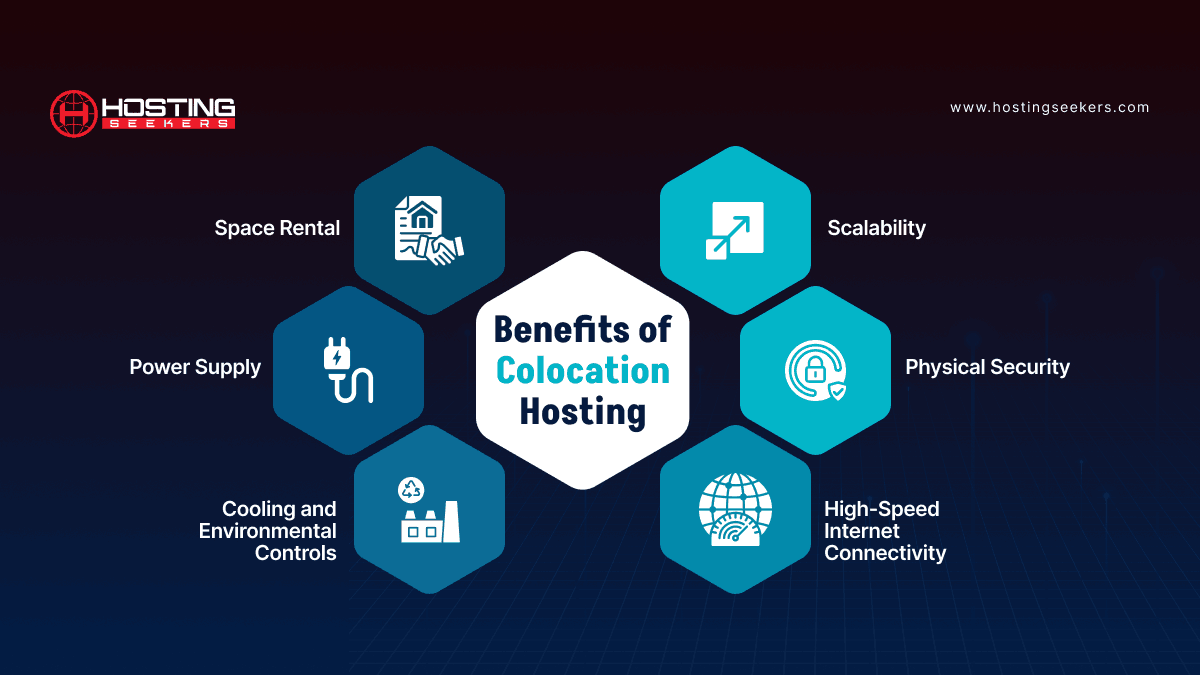
1. Space Rental
With colocation hosting services, you can lease the data center where your server hardware is stored. Depending on your needs, this space could be as large as a dedicated room or as small as a single rack unit. You decide how much space you’ll need for both your current setup and your future growth plans.
2. Power Supply
Colocated facilities ensure a dependable and redundant power supply that keeps your servers running. UPS devices and backup generators are utilized to control power irregularities and interruptions. Electricity usage can also be monitored and managed to improve productivity and reduce costs.
3. Reduced Capital Expenditure
Colocation eliminates the need for businesses to build and maintain their data centers. Instead of investing heavily in infrastructure, cooling, power systems, and physical security, companies can simply rent space in a colocation facility. This significantly reduces upfront costs while providing access to enterprise-grade infrastructure.
4. Improved Reliability and Uptime
Colocation providers typically offer redundant power supplies, high-speed internet connections, advanced cooling systems, and 24/7 monitoring. These features ensure maximum uptime and reliable performance, which is crucial for businesses that require continuous access to applications and data.
5. Cooling and Environmental Controls
Modern cooling technology is used in Colocation data centers to ensure that your devices are maintained at optimal temperature and humidity. HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) devices, in addition to hot and cold aisle containment methods, are utilized for effective heat dissipation control. Regular environmental monitoring ensures that your devices remain within a stable and secure environment.
6. High-Speed Internet Connectivity
Colocation hosting makes redundant, fast internet connections accessible. Data centers are equipped with many network pathways and internet service providers (ISPs) to ensure consistent and low-latency access. This robust internet infrastructure is crucial for businesses whose services and applications require fast and dependable network performance.
7. Physical Security
Security is highly valued in colocation server hosting, and data centers use multiple layers of physical protection. These include biometric access limitations, security guards, surveillance cameras, and restricted entry points. You can relax knowing that your equipment is protected from theft, physical threats, and illegal access, which is essential for your infrastructure.
8. Focus on Core Business
By outsourcing infrastructure management, businesses free up their internal IT teams to focus on innovation, strategy, and improving services rather than spending time on server maintenance, power backups, or facility management.
9. Scalability
Colocation hosting offers scalability options to accommodate your evolving business needs. You may quickly scale up by adding more space or altering your hardware configurations as your demands grow. Due to its flexibility, you can easily match your infrastructure to your business objectives without being constrained by the need of developing and operating a data center.
Pros and Cons of Colocation Hosting
Pros of Colocation Hosting:
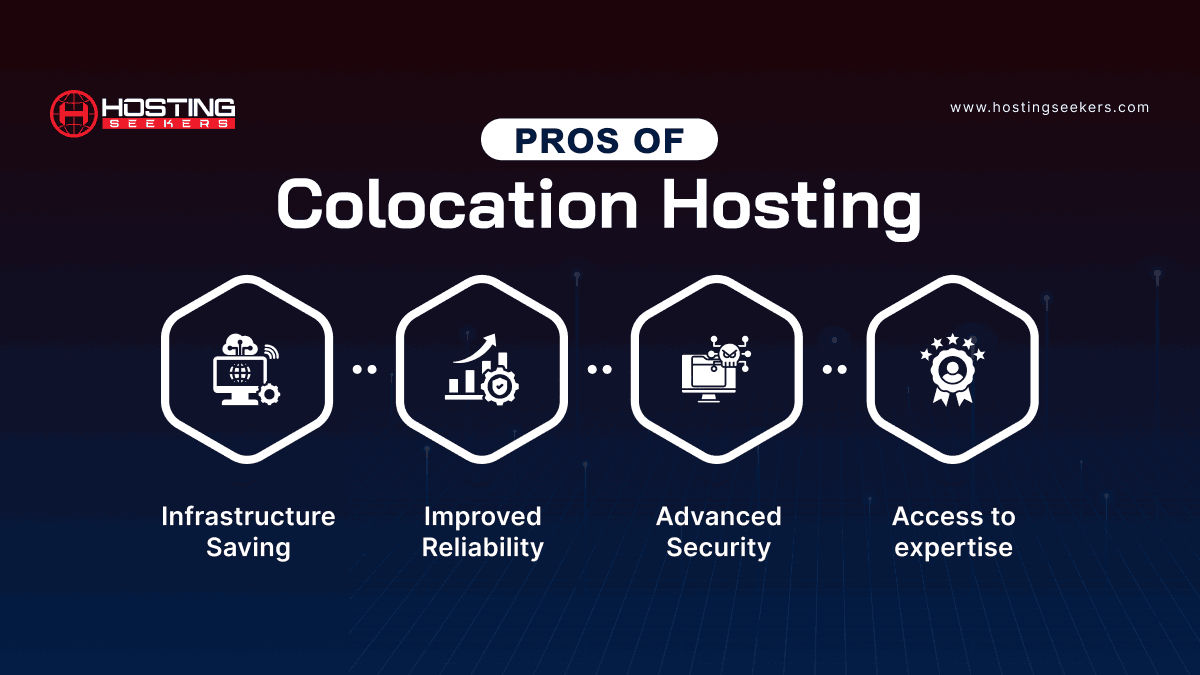
1. Infrastructure Saving
Colocation server hosting allows businesses to share cooling, security, and electric power costs with other users. Many companies consider this option viable due to the significant cost savings that arise from operating an internal data center.
2. Improved Reliability
Redundancy is a key developed design element of colocation facilities, including multiple power sources, sophisticated cooling systems, and backup generators. Therefore, as a result, corporate activity may have more excellent continuity than conventional in-house installation, which guarantees lower reliability and uptime.
3. Advanced Security
Colocation data centers utilize strong physical and cyber security measures, such as fire suppression systems, access controls, and analysis. Compared to on-premises data centers, these facilities are usually more secure, shielding infrastructure and sensitive data from several threats.
4. Access to Expertise
Color firms offer knowledgeable support and upkeep for the facility’s infrastructure by staffing it with skilled IT specialists. Businesses can also benefit from these people’s experience and knowledge without having to hire specialized employees.
Cons of Colocation Hosting:
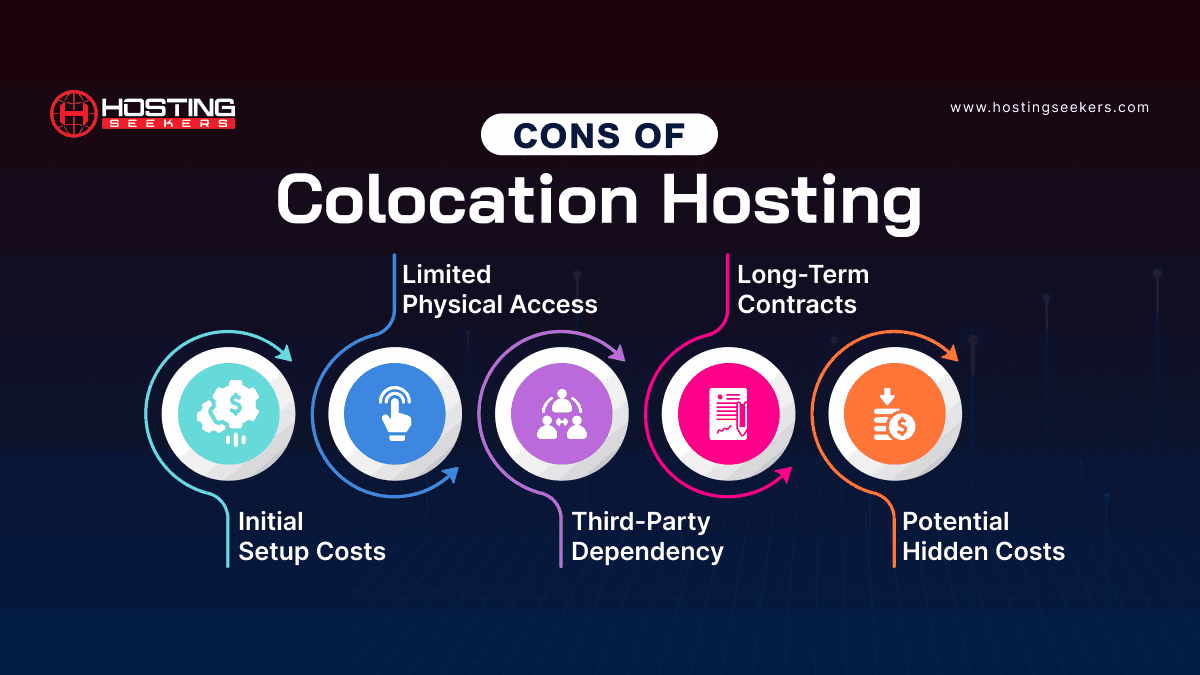
1. Initial Setup Costs
Although significant up-front costs may be associated with buying server equipment and moving it to the colocation center, colocation can result in long-term financial advantages. These up-front costs can be too much for startups or smaller companies to afford.
2. Limited Physical Access
Unlike on-premises data centers, colocated servers are situated at remote locations, preventing physical access. As a result, it may be challenging for businesses to perform in-person maintenance, updates, or troubleshooting without scheduling visits or relying on remote hand services.
3. Third-Party Dependency
The practice of relying on other vendors for infrastructure and essential services is called colocation server hosting. Problems with the supplier, such as inadequate customer service, security breaches, or service interruptions, could affect the company’s operations and potentially result in data loss or downtime.
4. Long-Term contracts
Long-term contracts linked to colocated web hosting agreements may prove limiting if a business’s demands change. These agreements could restrict companies’ freedom of choice and force them to accept terms and conditions that might not be appropriate for their changing needs.
5. Potential Hidden Costs
Colocation can be reasonably priced, but hidden fees for additional services like remote phone assistance, bandwidth overages, or excessive power consumption may be hidden. Companies should carefully review their colocation contracts because these costs may add up and offset some savings.
Who Should Use Colocation Hosting?
1. Medium to large businesses that already own servers
Companies that have already invested in powerful, enterprise-grade servers can save costs by collocating rather than purchasing additional infrastructure. Instead of maintaining their own data center, which can be very expensive, they can rent rack space, power, cooling, and bandwidth from a colocation provider.
2. Companies needing high security and uptime
Industries such as banking, financial services, healthcare, and SaaS providers rely heavily on compliance, data privacy, and uninterrupted service. Colocation centers offer advanced physical and digital security measures (like biometric access, surveillance, fire suppression systems, and DDoS protection) along with redundant power and network connections.
3. Organizations with in-house IT staff to manage and maintain servers
Since colocation only provides the physical environment (power, cooling, network, and space), companies still need skilled IT staff to configure, monitor, and troubleshoot their hardware. Businesses with dedicated IT teams benefit most, as they can maintain complete control over their servers while offloading the burden of managing the physical infrastructure.
Colocation Hosting vs Other Hosting Types
| Features | Colocation Hosting | Other Hosting (Dedicated, VPS, Shared, Cloud, Managed) |
| Hardware Ownership | You own and supply the server hardware. | The hosting provider owns and manages the hardware. |
| Initial Cost (CAPEX) | High (buying servers, networking equipment). | Low (no upfront hardware purchase). |
| Ongoing Cost (OPEX) | Predictable (rack space, power, cooling, bandwidth fees). | Varies – subscription or usage-based billing. |
| Control & Customization | Complete control over hardware, software, and networking. | Limited control; depends on hosting type (shared < VPS < dedicated < cloud). |
| Performance Isolation | Dedicated resources; no sharing with others. | Shared in VPS/Shared; isolated in dedicated and cloud. |
| Scalability | Requires adding/upgrading your hardware in the data center. | Upgrade plan, add VMs, or autoscale in the cloud. |
| Elasticity (on-demand scaling) | Low – scaling takes time and investment. | High in cloud, medium in VPS/dedicated; low in shared. |
| Provisioning Speed | Slow down the process of shipping and installing hardware in the data center. | Fast – minutes for VPS/Cloud, hours–days for dedicated. |
| Reliability & Redundancy | The facility ensures power/network redundancy; server redundancy is your responsibility. | Providers often include redundancy, backups, and failover solutions. |
| Security (Physical) | Strong – biometric/DC security; you can add private cages. | Strong at the provider’s data centers, but you rely on them. |
| Security (Management) | You manage OS, patches, firewall, and hardware security. | Provider manages hardware; you handle software (except managed hosting). |
| Network Control | Highest – direct BGP, cross-connects, peering options. | Limited to the provider’s setup; some flexibility in the cloud. |
| Scalability Across Locations | Limited to your chosen data center(s). | Cloud and some hosting types allow global distribution. |
| Operational Overhead | High – you handle maintenance, upgrades, and monitoring. | Low – provider manages most infrastructure. |
| Compliance & Data Sovereignty | Strong – choose specific certified data centers. | Strong for cloud/dedicated; weaker in shared hosting. |
| Physical Access | Available (you can visit the data center). | Not available; provider controls physical access. |
| Best For | Enterprises require control, compliance, hybrid setups, or the ability to handle steadily high workloads. | Businesses seeking scalability, low overhead, or cost-effective hosting without managing hardware. |
Top Colocation Hosting Providers
1. Hostinger
Hostinger, widely recognized for its shared, VPS, and cloud hosting services, also provides colocation solutions in select regions, making it a viable option for small to mid-sized businesses seeking affordable infrastructure. Its colocation services feature secure data centers equipped with redundant power and cooling systems, ensuring high reliability.
2. Kamatera
Kamatera is a colocation and cloud hosting provider that specializes in highly scalable solutions, offering businesses the flexibility to customize resources according to their specific needs. With data centers located across North America, Europe, Asia, and the Middle East, Kamatera ensures a broad global reach.
Its services include pay-as-you-go billing for both colocation and cloud solutions, combined with 24/7 technical support and rapid scaling options to accommodate growing workloads. This makes Kamatera an ideal choice for businesses seeking flexible colocation with hybrid cloud integration.
3. Equinix
Equinix is a global leader in colocation hosting, operating over 250 data centers worldwide and trusted by numerous Fortune 500 companies. It provides enterprise-grade colocation solutions designed for mission-critical workloads, offering direct access to major cloud providers such as AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud.
Equinix also delivers comprehensive global interconnection solutions that support hybrid IT environments, along with high-level physical and network security to protect sensitive data. This makes it an ideal choice for enterprises seeking world-class colocation with extensive global reach. While Equinix offers unmatched reliability and a vast data center network, its services tend to be more expensive compared to smaller colocation providers.
4. Ultahost
Ultahost is an emerging hosting provider gaining recognition for its reliable colocation services, offered alongside VPS, dedicated, and managed hosting solutions. Its colocation offerings feature enterprise-grade servers with redundant power, ensuring stable and secure operations.
Ultahost also provides managed colocation services with dedicated technical support, making it easier for businesses to maintain their infrastructure. With affordable packages compared to larger providers, Ultahost is well-suited for startups and small to mid-sized companies seeking a balance between cost and performance.
5. IONOS
Digital Realty is one of the largest colocation providers in the world, delivering secure and highly scalable colocation environments for enterprises. It operates over 300 data centers across more than 25 countries, providing extensive global coverage. The company offers interconnection with multiple cloud and carrier networks, enabling seamless hybrid cloud deployments.
Digital Realty also adheres to advanced compliance standards, including HIPAA, ISO, SOC, and PCI-DSS, making it ideal for large organizations in compliance-heavy industries such as finance and healthcare. With enterprise-grade security, broad global reach, and robust hybrid cloud connectivity, Digital Realty is a top choice for businesses with critical infrastructure needs.
What Should You Consider When Selecting a Colocation Hosting Provider?
When selecting colocation hosting providers, here are vital factors to consider:
1. Location: Choose a provider with data centers located strategically to minimize latency and meet your geographic preferences. Proximity to your end users can impact performance.
2. Security: Ensure the provider offers robust physical and network security measures, including surveillance, access controls, and fire suppression systems. Security certifications like ISO 27001 can be a good indicator.
3. Reliability: Check the provider’s uptime guarantees and the reliability of their infrastructure. Look for redundancy in power, cooling, and network connectivity to ensure high availability.
4. Scalability: Assess how easily you can scale your infrastructure as your needs grow. This includes the availability of additional rack space, bandwidth, and power.
5. Bandwidth and Connectivity: Evaluate the network connectivity options and bandwidth capacity. Ensure they provide enough bandwidth for your needs and have multiple, diverse network providers to avoid single points of failure.
6. Support: Consider the level of support provided. 24/7 technical support and on-site assistance can be crucial in resolving issues quickly.
7. Cost: Compare pricing models and ensure no hidden fees. Understand the costs for power, cooling, bandwidth, and any additional services you might require.
8. Customization and Flexibility: Ensure the provider can accommodate any specific technical requirements or customizations you might need for your hardware or infrastructure.
Conclusion
Companies often choose colocation hosting services for their data centers as it is affordable and convenient. It also gives them the necessary flexibility, scalability, and security for keeping their servers as well as infrastructure operating in a safe and efficient manner.
Colocation hosting allows to handle your servers and hardware yourself, meaning you can do any upgrading or downgrading at will. Such enables your business to grow rapidly.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q 1. What is colocation hosting?
Ans. Colocation hosting is a service that allows companies to lease storage in a data center where physical servers and networking devices can be installed. The data center provides the facility, including electricity, cooling, and physical protection, while the client is responsible for managing their machines.
Q 2. What is the difference between colocation hosting and dedicated hosting?
Ans. Colocation Hosting: In colocation, the client is responsible for the ownership and upkeep of their servers. The data center provides physical security, power, cooling, and space, while the hardware is managed and maintained by the client.
Dedicated Hosting: In a dedicated hosting environment, the service provider owns and operates these servers. The provider rents out a server to customers who handle all management activities, as well as upgrades and maintenance.
Q 3. What is website colocation?
Ans. In colocation data centers, Website colocation refers to the practice of hosting a company’s web servers. This way, the website gets an opportunity to use the strong infrastructure of the computer center, which is accessible to professional people, like speedy internet connections, redundancy, and also better security, while retaining the right to server hardware and software by the business itself.
Q 4. What is the difference between cloud hosting and colocation?
Ans. Cloud Hosting: The essential function of a cloud provider’s infrastructure is to deliver resources, including memory, CPU, and storage, which the users themselves do not manage. With such an arrangement, it becomes easy to scale up and down at any given time.
Colocation: Third-party data centers serve as physical homes for companies’ servers when they use colocation. As these companies have to maintain their equipment, any increase in demand necessitates actual changes, like adding more servers.
Q 5. Is colocation cheaper than cloud?
Ans. Here are some variables affecting the financial implications of colocation and cloud hosting:
Costs Upfront: Colocation typically involves a significant upfront investment in hardware, but subsequent expenses may be particularly high for organizations with stable and predictable needs.
Operational Costs: Although cloud hosting has lower initial expenses, high periodic subscriptions can escalate costs, particularly when resources are high or user consumption patterns are variable.
Q 6. What is the cost of colocation in India?
Ans. The cost of colocation in India varies depending on the provider, data center location, rack size, power usage, and additional services. On average, prices can range from ₹5,000 per month for a small 2U space to ₹1.7 lakh or more for a full rack with high power needs.
Q 7. Who is the largest colocation provider?
Ans. Globally, Equinix and Digital Realty are considered the largest colocation providers, operating hundreds of data centers worldwide. They serve enterprise clients with high-demand workloads, offering extensive interconnection, hybrid cloud integration, and enterprise-grade security.
Q 8. What are colocation hosting alternatives?
Ans. Alternatives to colocation hosting include cloud hosting, dedicated server hosting, and managed server hosting.




