VPS vs VPN – Choosing the Right Key for Your Online Needs
VPS Published on Date: February 28th 2024Among the plethora of tools and technologies available, virtual private servers (VPS) and virtual private networks (VPNs) stand out as two prominent solutions for various online needs. Understanding the nuances and differences between these technologies is paramount for making informed decisions about your online presence, security, and privacy.
In this comprehensive blog, we will delve deep into the difference between VPN and VPS, explore their benefits, compare their features, and provide insights to help you choose the right key for your online requirements.
Table of Content
VPS (Virtual Private Server) and VPN (Virtual Private Network) are two distinct technologies that serve different purposes in the realm of computing and networking
Virtual Private Server (VPS)
A VPS is essentially a virtualized server environment created within a larger physical server. It operates as an independent instance of an operating system, giving users the freedom to install and configure software as if they had their own dedicated server.
VPS hosting is commonly used for web hosting, development environments, and running applications that require dedicated resources. Users typically have root access to their VPS, allowing them to customize the server environment to suit their specific needs.
VPS hosting providers offer a balance between cost and performance. It offers more control and flexibility compared to shared hosting, but at a lower cost than dedicated hosting.
How does VPS Work?
A Virtual Private Server (VPS) works by virtualizing a physical server into multiple isolated virtual environments, each functioning as an independent server with its own operating system, resources, and configurations.
Here’s how it operates:
Virtualization Technology: VPS relies on virtualization technology, such as hypervisors (e.g., VMware, Xen, and KVM), to create multiple virtual instances within a single physical server. The hypervisor allocates resources from the host server, such as CPU, RAM, storage, and network connectivity, to each virtual server.
Isolation: Each VPS operates in isolation from other virtual servers on the same physical machine. This means that activities and configurations on one VPS do not affect others. Each VPS has its own file system, processes, users, and applications, providing a level of security and stability akin to a dedicated server.
Operating System: Users can choose their preferred operating system (OS) for their VPS, such as Linux distributions (e.g., Ubuntu, CentOS, and Debian) or Windows Server editions. The chosen OS is installed in the virtual environment and functions independently of the host server’s OS.
Resource Allocation: VPS hosting plans come with predefined resource allocations, including CPU cores, RAM, storage space, and bandwidth. These resources are dynamically allocated to each VPS based on the hosting plan and usage patterns. Users have the flexibility to upgrade or downgrade their resource allocations as needed.
Remote Access: Users manage their VPS remotely using administrative tools like SSH (Secure Shell) for Linux-based servers or Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) for Windows servers. They can install, configure, and maintain software applications, databases, web servers, and other services directly on their VPS.
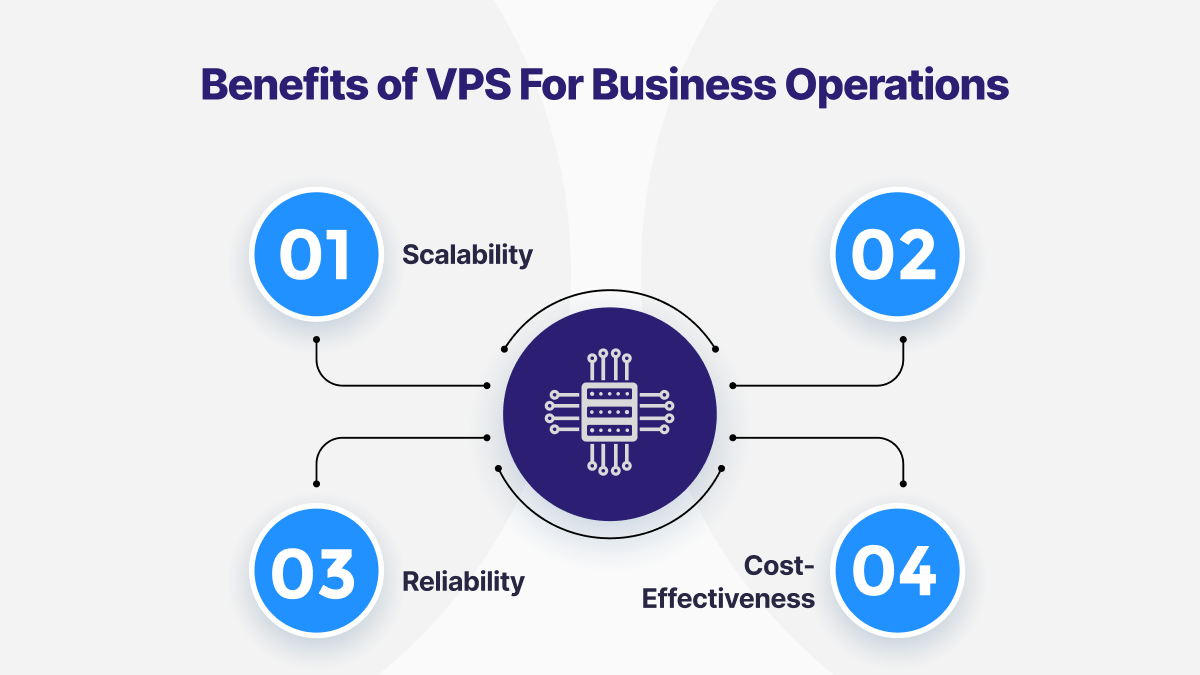
Benefits of VPS For Business Operations
Scalability: VPS offers scalability, allowing users to easily adjust resources such as CPU, RAM, and storage to accommodate changing demands without the need for physical hardware upgrades.
Control: With root access to their virtual servers, users have complete control over server configurations, software installations, security policies, and resource allocation, enabling them to customize their environments to suit specific requirements.
Reliability: VPS environments are isolated from one another, ensuring that performance issues or security breaches on one virtual server do not impact others. This isolation enhances reliability and stability, which are critical for business-critical applications and services.
Cost-Effectiveness: Compared to dedicated servers, VPS offers a cost-effective solution for businesses requiring dedicated resources and custom configurations without the high upfront costs associated with hardware procurement and maintenance.
VPN (Virtual Private Network)
A VPN is a secure network connection that encrypts data transmitted between a user’s device and a remote server, effectively creating a private network over a public network (typically the internet).
VPNs are commonly used to enhance privacy and security, especially when accessing the internet from untrusted networks such as public Wi-Fi hotspots.
They can also be used to bypass geographic restrictions by masking the user’s IP address and making it appear as though they are accessing the internet from a different location.
VPNs are widely used by individuals, businesses, and organizations to protect sensitive data and communications from interception or surveillance.
How Does a VPN Work?
VPN technology operates by creating a secure encrypted connection, often referred to as a tunnel, between the user’s device and a remote VPN server. This encrypted tunnel encapsulates data packets transmitted over the internet, preventing eavesdropping, interception, or tampering by unauthorized parties.
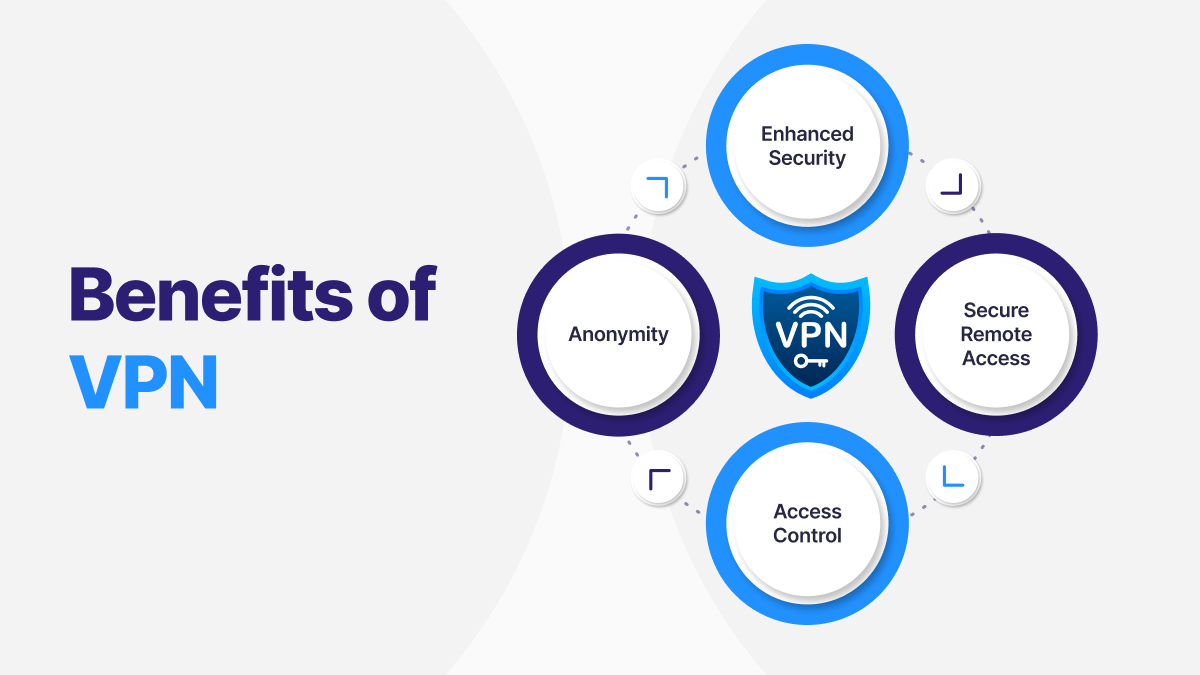
Benefits of VPN
Enhanced Security: VPNs encrypt data traffic, protecting sensitive information such as passwords, financial transactions, and personal communications from interception or surveillance by hackers, government agencies, or internet service providers.
Anonymity: By masking the user’s IP address and encrypting their internet traffic, VPNs preserve anonymity and privacy. This prevents websites, advertisers, or third parties from tracking users’ online activities or profiling their behavior.
Access Control: VPNs allow users to bypass geo-restrictions and access region-locked content by connecting to VPN servers located in different countries or regions. This enables users to access online services, websites, or streaming platforms that may be restricted or unavailable in their geographical location.
Secure Remote Access: VPNs provide secure remote access to corporate networks and resources for remote workers. This enables employees to connect to company servers, databases, and intranet portals from anywhere in the world.
What Do I Need: VPS or VPN?
VPN is essential for individuals and businesses concerned about online privacy, security, and unrestricted access to online content. Whether you’re accessing the internet from a public Wi-Fi hotspot, traveling abroad, or working remotely, VPN ensures that your data remains encrypted and secure, protecting against potential cyber threats, identity theft, and unauthorized surveillance.
A VPS is indispensable for businesses requiring dedicated server resources, customized configurations, and full control over their hosting environments. Whether you’re hosting websites, web applications, databases, or email servers, VPS provides the flexibility, scalability, and reliability needed to support diverse workloads and ensure optimal performance
How Much Do a VPN and VPS cost?
The cost of VPN vs. VPS services varies depending on factors such as provider, features, resources, and subscription plans. VPN services typically offer monthly or yearly subscription plans ranging from a few dollars to a premium price, depending on the number of features, server locations, and bandwidth allocation.
Similarly, VPS hosting costs vary based on the allocated resources (CPU, RAM, and Storage), operating system, management services, and additional features offered by the hosting provider.
VPS plans may start at a few dollars per month for basic configurations and scale up to higher-tier plans with more resources and advanced features at a higher cost.
VPN vs VPS: The Key Differences
While VPNs and VPS share some similarities in terms of providing privacy and security benefits, they serve different purposes and operate at different layers of the technology stack. .
Here are the key differences between VPN and VPS:
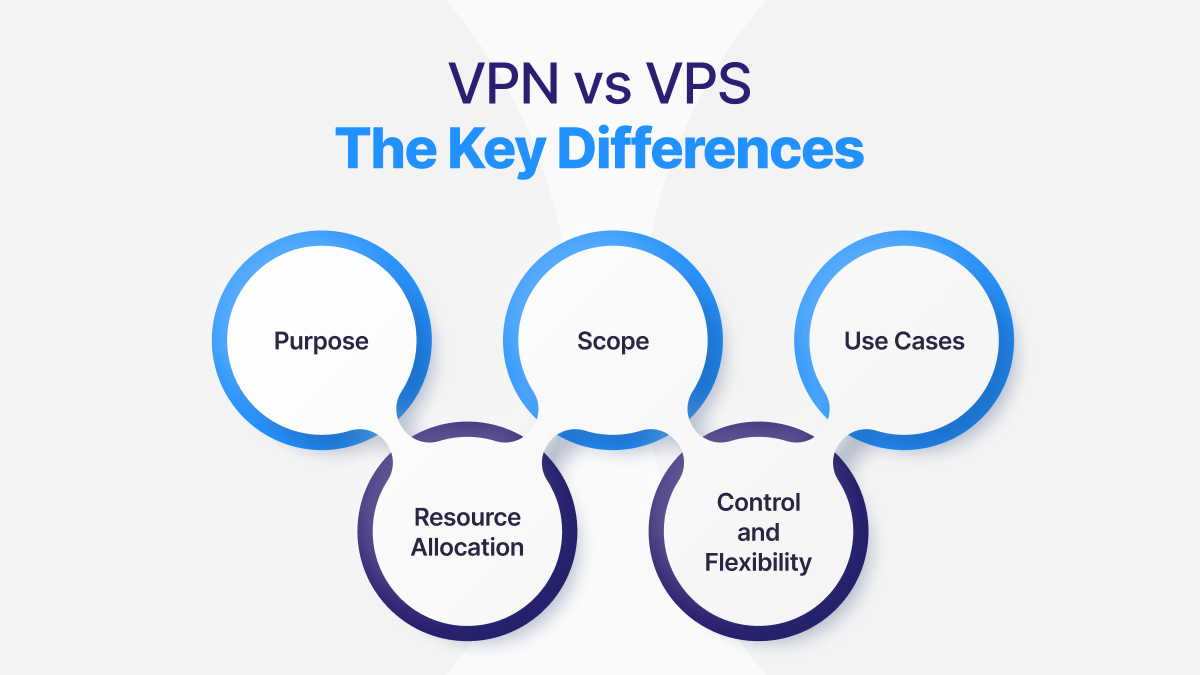
Purpose: VPNs primarily focus on securing network connections and encrypting data traffic, enabling users to access the internet securely and anonymously. In contrast, VPS provide virtualized server environments with dedicated resources and full control over server configurations, catering to users requiring hosting solutions for websites, applications, or services.
Scope: VPNs operate at the network layer, encrypting and tunneling data traffic between the user’s device and a remote VPN server. VPSs, on the other hand, operate at the infrastructure layer, providing virtual server instances with dedicated resources within a larger physical server infrastructure.
Use Cases: VPNs are commonly used for securing internet connections, bypassing geo-restrictions, accessing region-locked content, and ensuring privacy and anonymity online. VPSs are utilized for hosting websites, web applications, databases, game servers, email servers, and other services requiring dedicated server resources and customized configurations.
Control and Flexibility: VPN users have limited control over server configurations and resources. VPS users have full root access to their virtual servers, allowing them to install, configure, and manage software, security settings, and server environments according to their requirements.
Resource Allocation: VPNs typically offer shared resources across multiple users connected to the same VPN server, while VPSs provide dedicated resources allocated exclusively to each virtual server instance, ensuring consistent performance and reliability.
Use a VPS to Create Your Own VPN
Creating a personal VPN server using a VPS offers numerous benefits. This includes enhanced security, privacy, and customization options. Here’s how you can leverage VPS technology to set up your own VPN:
Step 1: Deployment of VPS Instance
The first step is to select a VPS provider and deploy a VPS instance. Providers like Amazon Web Services (AWS), DigitalOcean, and Linode offer various plans with different specifications and pricing options. Users can choose a VPS plan that suits their needs in terms of CPU, RAM, storage, and bandwidth.
Step 2: Selection of VPN Software
Once the VPS instance is set up, users need to select and install VPN software on the server. There are several open-source and commercial VPN solutions available, such as OpenVPN, WireGuard, and SoftEther VPN. Users should choose a VPN protocol and software that align with their security requirements and compatibility with their devices.
Step 3: Configuration of VPN Server
After installing the VPN software, users need to configure the server settings, including encryption protocols, authentication methods, and network settings. They can generate SSL/TLS certificates for secure communication between client devices and the VPN server. Configuration files and scripts provided by the VPN software make this process relatively straightforward.
Step 4: User Authentication and Access Control
To ensure security, users can set up user authentication mechanisms such as username/password authentication, certificate-based authentication, or multi-factor authentication. Access control lists (ACLs) can be configured to restrict access to the VPN server based on IP addresses or user roles.
Step 5: Network Routing and Firewall Configuration
Users may configure network routing and firewall rules to control traffic flow between the VPN server and client devices. This includes setting up split tunneling, which allows users to route only specific traffic through the VPN server while directing other traffic directly to the internet.
Step 6: Client Configuration
Once the VPN server is set up, users need to configure their client devices (e.g., computers, smartphones, tablets) to connect to the VPN server. This typically involves installing VPN client software and importing configuration files provided by the VPN server administrator. Users can then connect to the VPN server securely from anywhere with an internet connection.
Conclusion
VPS and VPN are invaluable tools for individuals and businesses seeking to optimize their online presence and security. Whether it’s hosting websites, securing data transmission, or bypassing geo-restrictions, VPS and VPN offer versatile solutions tailored to diverse use cases. By understanding their functionalities, benefits, and differences, users can make informed decisions to meet their specific requirements effectively.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
Q 1: What is the main difference between a VPS and a VPN?
Ans. A VPS is a virtualized server environment that provides dedicated resources and control over server configurations. It is ideal for hosting websites or applications. On the other hand, a VPN is a secure connection that encrypts data traffic. It ensures privacy and security while browsing the internet.
Q 2: When should I use a VPS?
Ans: You should consider using a VPS when you need dedicated server resources, customized configurations, and full control over your hosting environment. VPS is suitable for hosting websites, applications, databases, or running specific software that requires isolated resources.
Q 3: What are the benefits of using a VPS?
Ans: The benefits of using a VPS include scalability, control over server configurations, reliability, and cost-effectiveness. With a VPS, you can easily upgrade or downgrade resources as needed, customize server settings, ensure consistent performance, and enjoy dedicated resources at a fraction of the cost of a dedicated server
Q 4: When should I use a VPN?
Ans: You should use a VPN when you prioritize online privacy, security, and unrestricted access to online content. VPNs are essential for encrypting data traffic, protecting against cyber threats, preserving anonymity, and bypassing geo-restrictions to access region-locked content.
Q 5: What are the benefits of using a VPN?
Ans: The benefits of using a VPN include enhanced security, anonymity, access control, and secure remote access. VPNs encrypt data traffic, safeguarding it from interception or eavesdropping, mask the user’s IP address, provide anonymity while browsing online, bypass geo-restrictions, allow access to region-locked content, and facilitate secure connections for remote workers accessing corporate networks.