SSD vs SAS vs SATA: Which Is Better For A Dedicated Server?
Comparison Updated on : June 30, 2025Summary: SSD vs. SAS vs. SATA drives in detail to determine which of these three is ideal for your dedicated server. Read to know if SSD & SAS Drives are better than SATA.
Data is the driving force behind modern Internet applications. In a connected world where everyone wants everything instantly, the speed at which data is transferred to and from your application can make or break it. And that is why choosing the right hard drive is crucial for your dedicated servers.
When it comes to choosing the right storage and disk performance option, you should consider the core requirements of your dedicated server.
The deciding factors for storage disks are rotation speed, storage and cache capacity, and cost. When it comes to data storage, SAS vs. SSD vs SATA are prominent names. While all these serve the same purpose of data transfer, their designs and capabilities vary. So, which of these is best suited for your dedicated server?
Before we discuss further on this, we must first learn more about these three different forms of drives.
Let’s get started.
What is a SAS (Serial Attached SCSI) Drive?
This type of drive connects to the disk drive through a point-to-point interface. Admins typically use it on higher-end servers and workstations. SAS functions on a dual-port and offers higher capacity. In case of any controller failure in SAS drives, the redundancy remains high with uninterrupted performance.
The SAS built-in comprises:
- 2 conductors, each for sending and receiving data
- Ground cables between the conductors to minimize interference.
Typically, SAS drives are used to deliver high enterprise performance and sustain heavy loads.
On the technical front, it offers:
- Rotation Speed: Ranges between 10,000 RPM and 15,000 RPM
- Reliability: MTBF (Mean time before failure) is 2 million hours at 40 degrees Celsius.
- Storage: Mostly offers including 300GB, 600GB, 900GB, 1.2TB, and larger. )
- Access Rate: The data transfer rate is 15 Gb/s.
Advantages Of SAS Drives
- Minimizes storage failure rates by reducing the number of physical interconnects.
- Delivers high performance with 15000 RPM, which results in a greater bandwidth and better drive performance.
- The physically small structure allows data centers to improve their energy efficiency. In addition, their smaller footprint allows the installation of more drives per system for greater redundancy and performance density.
- Higher scalability because of its capacity to scale over 100 drives.
- Valuable when speed is more important than capacity.

What is an SSD (Solid State Drive)?
This type of disk drive has no mechanical moving components and delivers great performance. Zero moving parts also mean fewer risks of failure and increased power efficiency.
It is a ‘solid’ investment if you are looking for speed, as these offer 100 times greater throughput than traditional drives. SSD drives are reliable and ideal for high-frequency transactional data like CRM, databases, or bank transactions.
On the technical front, SSD offers:
- Read/Write Speed: Up to 500-600 MB/s
- Reliability: MTBF is 2 million to 5 million hours.
- Storage: Offers 240GB to 15.36TB.
- Access Rate: The data transfer rate is between 500 MB/s to over 7,000 MB/s
Advantages Of SSD Drive
- These are shock-resistant because they don’t have any moving components like spindles.
- Delivers unbeatable speed and consumes less power. Hence, a low carbon footprint.
- Less prone to mechanical damage.
- Low operational cost.
What is a SATA (Serial Advanced Technology Attachment) Drive?
SATA uses a bus interface to connect with mass storage components like hard disks or optical drives. These are known for their outstanding storage capacity and power efficiency. Their higher storage capacity makes them ideal for file sharing, web, email, backup, and archival data. These are also used in low-end servers.
On the technical front:
- Rotation Speed: Ranges between 10,000 and 15,000 RPM: These higher speeds are typically found in enterprise-level drives
- Reliability: MTBF is 700,000 hours to over 3.5 million hours at operating temperatures between 25°C and 45°C)
- Storage: Offers more than 4 TB of storage.
- Access Rate: Up to 6 GB/second.
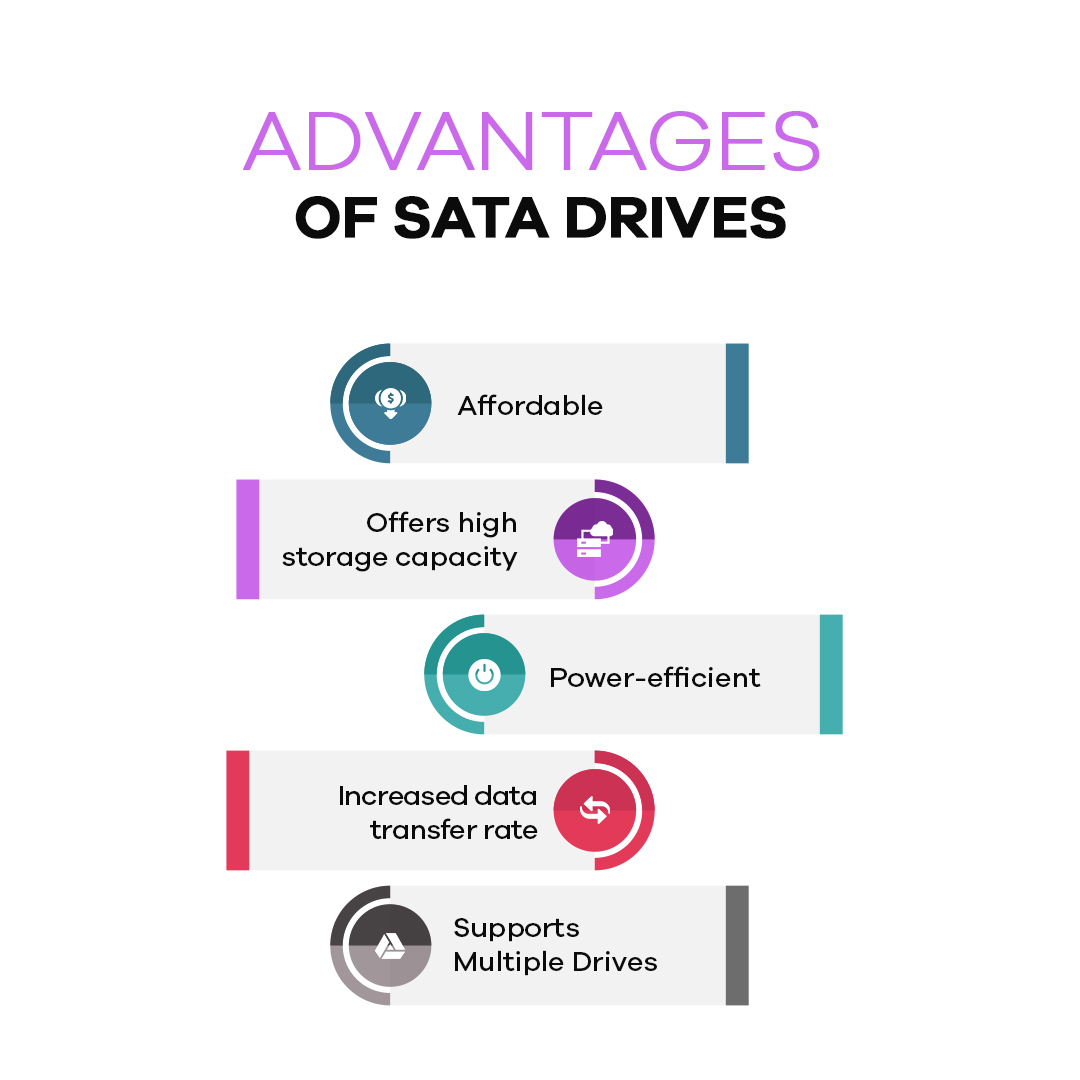
Advantages Of SATA Drives
- SATA drives are affordable, which is why they are common among consumers.
- These offer high storage capacity.
- Power-efficient.
- Increased data transfer rate
- Supports Multiple Drives
What are the Differences Between SSD vs SAS vs SATA?
So, here are the main points of differences between SSD vs SAS vs SATA:
| Factors | SAS | SSD | SATA |
| Speed | 10,000 RPM and 15,000 RPM | Read/Write Speed Up to 500-600 MB/s) | 10,000 and 15,000 RPM |
| Storage | 300GB, 600GB, 900GB | 240GB to 15.36TB. | More than 4 TB |
| Power | Comparatively less efficient than SATA | Comparatively less efficient than SATA | Power-efficient |
| Price | Expensive | Expensive | Affordable |
| Usage | High-end servers and workstations | high-frequency transactional data | Low-end servers, email, file sharing, backup, archival data |
| Performance | Best | Better | Good |
Sas vs SSD Performance Chart (Add)
To compare the performance of SAS and SSD, following test can be conducted:
- 1 HDD: All 6 virtual machines (VMs) are hosted on a single 15,000 RPM SAS HDD drive.
- 2 HDD: The 6 VMs are distributed across two 15,000 RPM SAS HDD drives, with 3 VMs allocated to each drive.
- 3 HDD: The 6 VMs are divided among three 15,000 RPM SAS HDD drives, with 2 VMs assigned to each drive.
- SSD: All 6 VMs are stored on one 15,000 RPM SAS HDD, while a separate SSD is utilized exclusively as a cache folder.
Comparison of System Usage among different HDD/SSD drive combinations
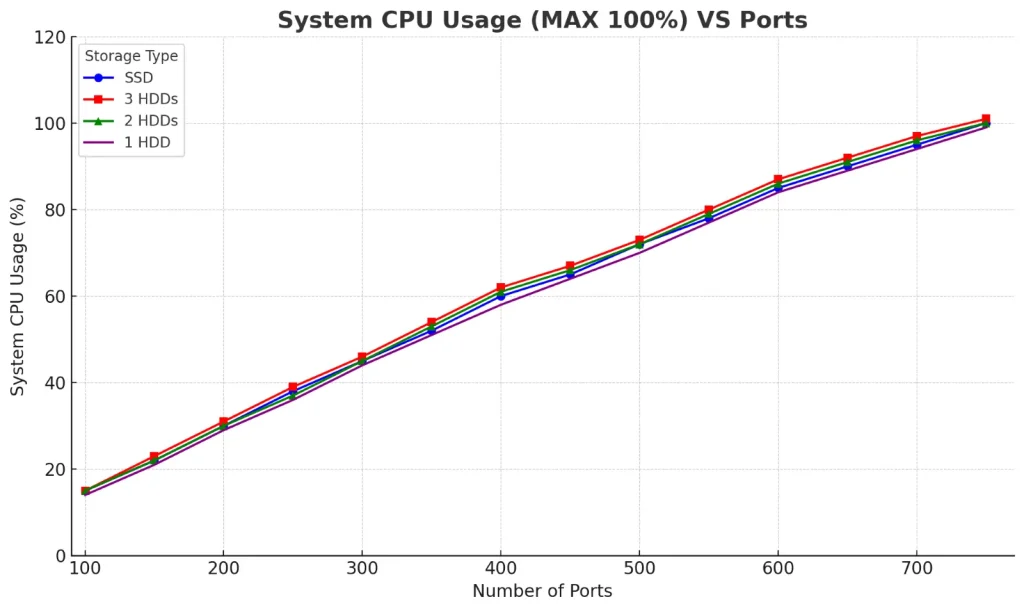
1. X-axis: Number of Ports
2. Y-axis: System CPU Usage (%)
3. Legend:
- 🔵 SSD (Blue, circles)
- 🔴 3 HDDs (Red, squares)
- 🟢 2 HDDs (Green, triangles)
- 🟣 1 HDD (Purple, crosses
The graphs below compare max jitter and max delta for HDD/SSD drive combinations:
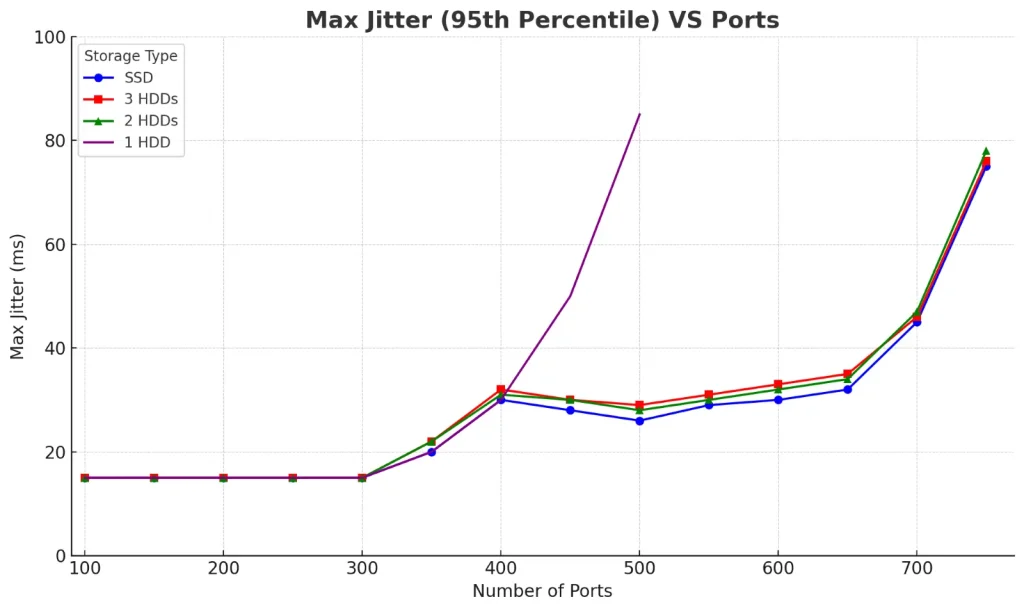
1. X-axis: Number of Ports
2. Y-axis: Max Jitter (milliseconds)
3. Legend:
- 🔵 SSD – Blue line with circles
- 🔴 3 HDDs – Red line with squares
- 🟢 2 HDDs – Green line with triangles
- 🟣 1 HDD – Purple line with crosses (data only up to ~450 ports due to missing values)
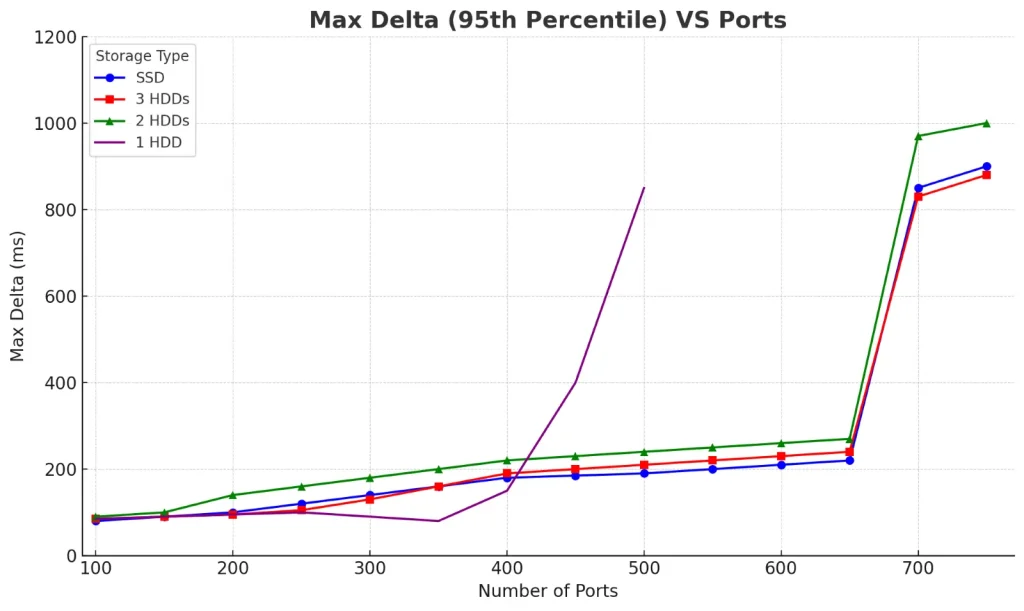
- 🔵Blue line with circles: SSD
- 🔴Red line with squares: 3 HDDs
- 🟢Green line with triangles: 2 HDDs
- 🟣Purple line with X markers: 1 HDD
Are SAS drives really better than SATA?
While the decision to choose between SAS and SATA is entirely requirement-specific, most businesses opt for SAS for their mission-critical websites. This is because SAS (and even SSD) offers better throughput, speed, and a lower risk rate. On the contrary, if your focus is on storage than reliability and speed, SATA is your option. So yes, SAS drives are better than SATA drives.
Conclusion
We hope this blog has unraveled all your doubts about the types of hard drives SSD vs. SAS vs. SATA and which hard drives you should choose for your dedicated server. So, make the right choice to ensure the top performance and longevity of your server.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q 1. Are SAS hard drives better than SATA?
Ans. Both SAS and SATA drives are used to connect computer storage units like media drives or hard drives to motherboards. SATA drives offer larger storage than SAS and are pocket-friendly. These are generally used in personal computing. On the other hand, SAS drives are faster and more reliable than SATA drives and hence are ideal for servers. So, SAS hard drives are definitely better than SATA.
Q 2. Which is better, SAS or SSD?
Ans. This depends on your requirement! While SAS drives are suitable for enterprise server storage, SSDs are ideal for high-frequency transactional data. Both SAS and SSD are great at performance and reliability. However, SSDs are shock-resistant and consume less power than SAS. Cost-wise, SAS drives are affordable than SSDs.
Q 3. What is the benefit of SAS drives?
Ans. SAS drives deliver high performance with 15K RPM, which results in a greater bandwidth and better drive performance. These are highly reliable, faster, and energy-efficient.
Q 4. How much faster is SAS than SATA?
Ans. SAS drives are able to rotate much faster, up to 15000 RPM than SATA drives (typically 7.2K RPM). Hence, SAS drives may be substantially more than 2 times faster than SATA.
Q 5. How Do I Choose a Hard Drive For My Server?
Ans. When choosing the right hard drive for a server, you should consider:
- What do you need: an Internal or external hard drive.
- Storage Capacity you need
- Performance (latency, rotation speed, positioning speed)
- Interface
- HDD or SSD
Q 6. Do SAS drives use more power?
Ans. Yes, SAS consumes more power as compared to SATA. SAS drives can use at least two times the signaling voltage than SATA or ATA drives. And more power means higher running costs.
Q 7. What is a SAS SSD?
Ans. A Serial-Attached SCSI solid-state drive or SAS SSD is a caching device with NAND flash-based storage. It uses the SAS interface to connect to the host computer. SAS SSD is designed in a way to fit in the same slot as a hard drive (HDD).