NVMe vs SATA – Which is Better?
Comparison Published on Date: February 10th 2022If you want to upgrade your system storage, you have got two recent options, NVMe and SATA. But in the comparison, NVMe vs SATA, which is a better option for you? Let’s find out.
The biggest upgrade you can make to your laptop or desktop is faster storage. And when it comes to faster storage, solid-state drives (SSDs) have outshined traditional hard disk drives (HDDs) a long time back. But what about choosing between the two most popular SSDs – NVMe and SATA? Clear all confusions as we compare NVMe vs SATA in our today’s blog.
Let’s begin with knowing a little about both these SSD drives one by one.
What is NVMe?
Non-Volatile Memory Express or NVMe is the newest software protocol for PCIe (Peripheral Component Interconnect Express) SSDs. Introduced in 2013, NVMe allows to read and write data through PCIe. NVMe acts as a layer between the device driver and the PCle device and is designed to address the needs of computers using PCIe-based solid-state storage.
If we go by the full term, “non-volatile memory” refers to the memory that retains data even when the system or power is turned off, and “express” means the data travel on the PCle bus on your system’s motherboard, which provides high-speed data transfer and low latency.
In current times, when applications have become vastly more complex and resource-dependent, consumers and businesses still expect lightning-speed response times. Moreover, performance and data endurance is important more than ever. To fulfill this need for low-latency user experience and high bandwidth, the NVMe interface accesses flash storage via the PCI Express (PCIe) bus to support thousands of parallel command queues. This makes NVMe much faster than HDDs (hard disks) and even traditional all-flash architectures, that utilize a single command queue.
NVMe SSD is impacting businesses significantly allowing them to control what they can do with data, specifically fast data for emerging technologies and real-time analytics.
Features of NVMe SSD are:
- Uses flash technology for fast read-write.
- Can send up to 64K commands per queue that consume low CPU cycles.
- Communicates with system CPU directly.
- Has latency of about 2.2 microseconds.
- Performs over 1 million IOPs (Input/output Operations per Second).
What Does An NVMe SSD Look Like?
If you visit a store to buy an NVMe-based drive, you would need an M.2 gum stick, which describes how a drive looks. M.2 illustrates the drive’s form factor and has up to 1 TB of storage. However, these are so tiny that you can hold them in between your thumb and index finger.
Since M.2 drives connect to M.2 PCle slots, it supports up to four lanes of data transfer. While usually, these drives are NVMe-based, you can also find M.2 SATA III drives. So, before you make your purchase, make sure to read the packaging carefully.
Pros & Cons of NVMe SSD
Let us now look at the advantages and disadvantages of NVMe SSD:
Advantages of NVMe SSD
- Provides superior speed & storage.
- Provides high-level compatibility as it directly communicates with CPU
- NVMe-based SSDs are compatible with all major operating systems regardless of form factor.
- NVMe aids tunneling protocol that deals with data privacy concerns.
- Supports much higher bandwidth than SAS or SATA.
- NVMe provides end-to-end latency of fewer than 10 microseconds, which also includes software stack.
Disadvantages of NVMe SSD
- NVME SSD is expensive and is priced much higher than standard 2.5″ SSD devices.
- Upgrading storage systems is difficult as older computer systems do not support legacy NVMe.
- Since client PCs utilize NVMe M.2 format, it limits the drive selection as compared to other available solutions.
- This isn’t a cost-effective solution for storing a large volume of data.
When To Choose NVMe?
You can opt to choose NVMe SSD in the following situations:
- If you are planning to build a gaming PC or a high-end workstation.
- If you are building a server for hosting a storage-intensive application.
- If you do not have any budget constraints.
What is SATA?
Serial ATA or SATA is a connection interface that SSDs use to communicate with the system. Created in 2003, it uses the same interface as hard drives. While SATA is the lowest grade SSD, a system that uses SATA SSD still offers 3 to 4X bandwidth similar to a system using a hard drive. Since SATA SSDs were launched in 2003, the chances of finding users using them are high.
A SATA SSD can boot and read and write data much faster than its HDD counterpart. Further, SATA SSDs have a lifespan of about 10 years, which makes their longevity higher than HDD drives. You can notice the difference in the speeds of SATA SSDs and HDDs when turning on your PC, switching between tasks, or opening an application
However, SATA SSDs are costlier than HDDs, costing about double as much for the same storage capacity.
The most common type of SATA SSD is the 2.5-inch drive, which can be used on older computers. While the average speed of SATA SSDs is about 500-550 Mbps, it can increase up to 600 Mbps or 6 Gbps.
SATA SSDs are ideal for casual home users as they are faster (not more than NVMe) and cheaper.
Features of SATA SSD are:
- Compatible with most desktop or laptop systems, even a decade-old system.
- Have worse relative performance with a transfer speed between 4.8Gb/s (600MB/s) to 6Gb/s (750MB/s) depending upon the physical overhead caused during encoding the data for transfer.
- These are usually cheaper as compared to their PCle counterpart.
What do SATA SSDs Look Like?
SATA SSDs come in various form factors in terms of their physical size, connector, and shape:
- 2.5 inch – This is the most common type of SATA SSDs. They have the same physical shape and size and even can fit into the same space as a traditional hard drive.
- M.2 SSDs – These are thin sticks that fit into the motherboard through an M.2 connector or slot.
- Add-In Card (AIC) – These are among the fastest SSDs and are seen on desktops only. Their larger surface area makes them ideal for use in RAID controllers or GPUs.
- U.2 – Though, U.2 (see image) looks like SATA SSDs, it uses a different speed data and connector via the speedy PCIe interface. These are costlier and have more storage capacity than M.2 SSD.
Pros & Cons of SATA SSD
Let us consider the advantages and disadvantages of SATA SSD.
Advantages of SATA SSD
- SATA has been known for decades for its extensive support on different form factors and hardware. This makes it remarkably compatible with a lot of new and older devices, even from the early 2000s.
- SATA SSDs are relatively inexpensive as these can be easily obtained and have lower levels of performance than spinning media.
- It does not occupy a slot on the system motherboard.
- Has a well-established format.
Disadvantages of SATA SSD
- SATA is the slowest storage transfer protocol; hence ideal for older storage devices and not modern or upcoming devices.
- Does not suit busy, data-intensive environments that rely on fast data transfers and low latency.
- Some M.2 devices that use SATA slots and command sets perform much more slowly than their NVMe counterparts.
- It needs a bay for installation.
When To Choose SATA SSD?
- SATA SSD is a preferable option for workloads where low cost & larger capacities are the main priority. For example, you can use SATA SSD for tasks like archiving data, keeping backup solutions, storing little-used files, etc. In short, to perform tasks where the transfer speed is not a priority.
- When you are required to connect drives in a large number.
COMPARISON: NVMe SSD vs SATA SSD
Both SATA and NVMe are storage interfaces used by SSDs to transfer data between SSD and CPU. But then where do these differ?
Let’s dig deeper into NVMe vs SATA.
1. Performance
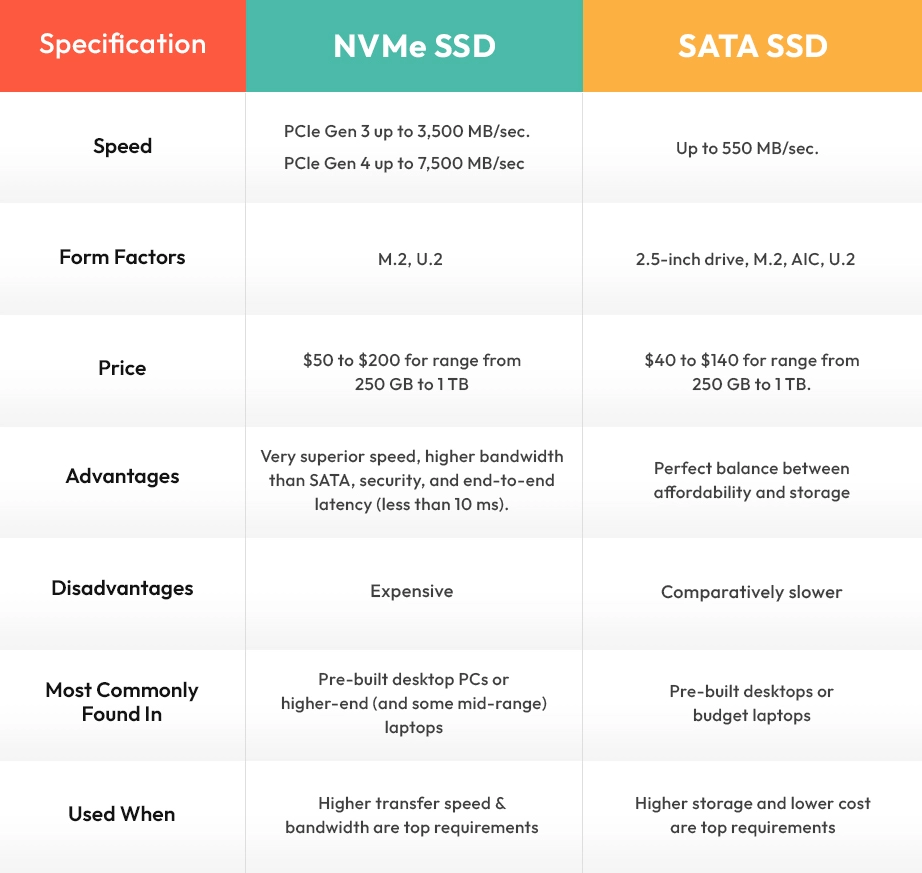
Superior SATA SSDs read at the maximum speed of 600 MB/s in an ideal situation. The speed of the latest SATA III typically falls close to or significantly under 600 MB/s.
Comparatively, NVMe SSDs read at a faster speed of approx. 3500MB/s. The reason for this faster read and write speed is primarily due to its structure and the way it connects with other PC components. NVMe has a parallel structure that complements the structure of CPUs, applications, and platforms. This parallelism allows more commands to simultaneously flow between the components, using an optimized path.
Also, NVMe was specifically designed for the NAND technology used in SSDs. This means both the technologies can benefit from each other and work together in sync, which makes a drive perform faster.
This makes NVMe SSDs score higher in terms of performance. Gamers, computer users, and photographers who use data-heavy applications highly benefit from NVMe SSDs.
2. Parallelism
Parallelism in NVMe SSDs is its ability to run multiple operations at once via multiple threads. The rapid I/O of NVMe significantly increases its processing speed.
Typically, NVMe drives have a queue depth of 64,000 and support 64K queues. On the contrary, SATA SSDs have a queue depth of 32 with a single command queue. This means SATA can, at max process up to 32 I/O requests at any time.
3. Compatibility
SATA was created in 2000 in comparison to PCIe that came in 2003. This makes SATA a slightly older interface than PCIe. Hence, SATA was adopted by organizations earlier which is why it has a broader range of compatibility than PCIe.
An older system that needs to be upgraded may not have a PCIe slot or its existing slot may not be compatible with the latest SSDs. Comparatively, a SATA cable is compatible with most systems made in the last two decades.
So, in case you are unsure about the connection type, your system has, opt for a SATA SSD. Most probably, it will work with any system functioning at present.
4. Security
NVMe SSDs offer robust protection to your data & information by reinforcing industry-standard security solutions such as the Enterprise SSC and the Opal SSC. Besides, these offer a security feature to prevent unintended changes after the system provisioning and protect the system from malicious or unintentional changes.
However, in the case of SATA SSDs, there’s no built-in encryption in most consumer drives unless you choose the pricier high-end options.
5. Price
While the cost for both SSDs greatly depends on capacity and size, SATA is still more affordable than NVMe. Compared on a per-gigabyte basis, the PCIe SSD tends to be more expensive than SATA SSD. So, if you are on a budget, you should prefer a lower-cost SATA SSD to get the most bang for the buck.
Comparison Table: SATA vs NVMe
Final Verdict – NVMe Vs SATA
So, when it comes to NVMe SSD vs SATA SSD, your choice greatly depends on two key factors: Your intention, and your budget. For instance, if budget is your priority, go with SATA SSD. However, if you need maximum performance for continual file transfers, NVMe SSD is your best bet.
Please note here that both NVMe & SATA are most convenient to be used in the M.2 form factor. Hope this article on SATA vs NVMe will help you make the right decision.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q 1. When to use NVMe vs SATA SSD?
Ans. SATA SSD is ideal for use when higher capacity and lower cost are the top preferences. But if you need higher transfer speeds & bandwidth without any budget constraints, you should go with NVMe SSD.
Q 2. What is a SATA Hard Drive?
Ans. A SATA hard drive is a kind of rewritable mass storage device found inside computers, laptops, and servers. Technically, SATA or Serial Advanced Technology Attachment is a computer bus interface, which connects host bus adapters to mass storage devices.
Q 3. Is SATA better for gaming than NVMe?
Ans. While an NVME SSD does not increase your gaming performance, at least FPS-wise. However, it will definitely give you an edge over SATA in terms of loading speed
Q 4. Are NMVe and SSD the same?
Ans. No, SSD and NVMe are not the same. SSD stands or solid-storage devices are non-volatile storage devices that use flash memory to store data frequently. On the other hand. NVMe or non-volatile memory express is a software interface used to access stored data. Also, SSD is a part of hardware whereas NVMe is software that can be installed into the computer.
Q 5. M.2 SATA vs NVMe – Which is better?
Ans. M.2 SATA and NVMe are the two most popular types of SSDs today. When comparing M.2 SATA vs NVMe, the main differences lie in their speed and cable clutter. When buying an M.2 device, you must be careful. While these may look identical, some M.2 form factor devices still use SATA connections without the need for cables.
Another thing to consider here is both SATA M.2 and 2.5-inch SSDs perform at the same speed. However, if the drive uses an NVMe connection, there will be an increase in its performance.