IaaS vs PaaS vs SaaS | Top Cloud Service Models 2026
Cloud Industry Updated on : December 31, 2025Read our blog on IaaS vs PaaS vs SaaS & get to know the key differences between the three popular cloud services models.
Table of Content
Cloud computing has become the standard for businesses of all sizes. It offers a number of advantages over traditional on-premises IT, including scalability, flexibility, and cost savings.
There are three main types of cloud computing services: infrastructure as a service (IaaS), platform as a service (PaaS), and software as a service (SaaS). Each type offers a different level of control and responsibility to the user. In this blog post, we will discuss the differences between IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS.
A recent study by Gartner predicts that global spending on public cloud services will grow 18.4% in 2021 to $304.9 billion, from $257.5 billion in 2020.
Flexibility, scalability, ease-of-configuration, savings, and security, this is all that cloud services offers.
IaaS vs PaaS vs SaaS: 3 Core Service Models
In this write-up, we will delve into three different cloud service models IaaS vs PaaS vs SaaS comparison along with their examples.
1. IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service)
IaaS is a cloud computing solution that offers provisioning, managing, and computing service resources over the Internet, like web servers, storage, devices, and virtualization devices. Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) offers the technologies and capabilities of quality data centers even without any significant capital investment of IT infrastructure. IaaS users can access this infrastructure just with a simple dashboard or API and do not need to manage this infrastructure physically as it’s the responsibility of the cloud service provider.
This cloud service model provides a lot of flexibility to businesses as it allows them to purchase on-demand hardware, software, storage space, and other required resources. This service model helps to increase the business security, redundancy, scalability, and efficiency while having complete control over the infrastructure.
Besides, companies can outsource the infrastructure and prevent themselves from manual work like configuration, server maintenance, and downtime as well. Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) can be used for several purposes like deploying website-based applications, monitoring CRM, Big Data Analysis, Data Storage, Disaster and Backup Data Recovery, etc.
Examples of IaaS
- Amazon Web Services (AWS)
- VMware
- DigitalOcean
- Linode
- Rackspace
- Microsoft Azure
- Google Compute Engine (GCE)
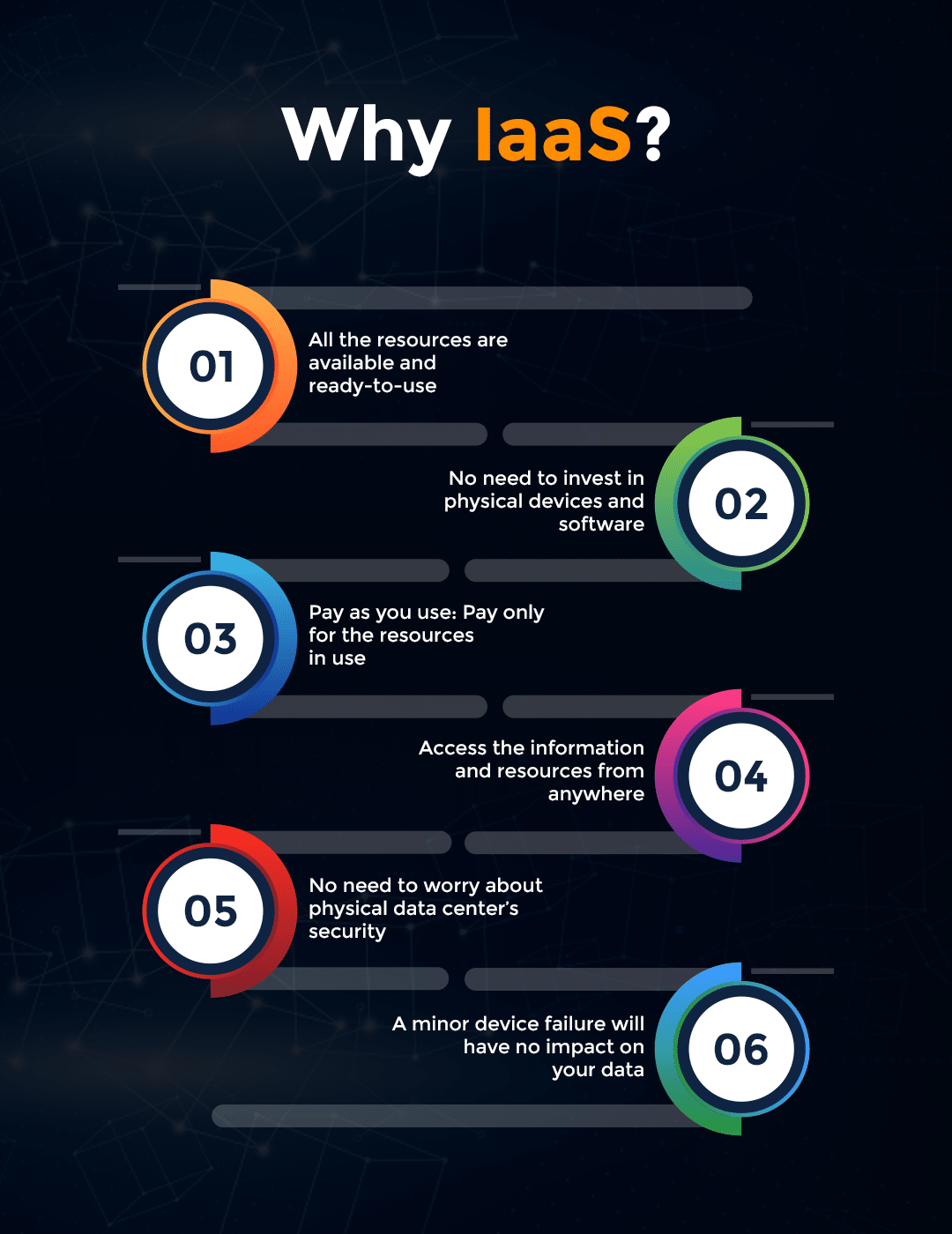
Main Benefits of Using IaaS
- Full Control: Complete control and manage their entire infrastructure
- Extend Storage: Resources can be purchased as per business demand without investing a lot
- Automate Business: Full access to business automation and scalability
- Instant Fixes: Less downtime, instant maintenance, and recovery from outages
- Super Fast Website: Increased website speed and flexibility to add up new functionalities
Challenges of IaaS
- Features Limitation: IaaS features vary according to the service provider
- Downtime: Service performance issues might affect in public cloud
- Compatibility: Complex management and interoperability between environments
2. PaaS (Platform as a Service)
PaaS is another popular cloud service model that offers a ready-to-use development environment for developers to stay focused on writing and implementing advanced code to create highly customized applications. This platform is delivered via the web and allows developers to create highly scalable and high-quality applications without worrying about storage space, OS, software updates, and more. Basically, it provides simple frameworks for developers to code, develop, manage, distribute, and deploy applications.
This type of service model simplifies the software development and deployment processes. Moreover, it can be accessed by several users in a single time frame through the same development application, and it combines several web services, database engines, and operations to make application development easier for the developers.
PaaS is a cloud-based service platform and so it accelerates the software development cycle by default. However, PaaS users can only control the applications they have built over that platform. Therefore, if any software or OS-related issue arrives, they cannot do anything about it and they can face its consequences as well in the applications they have built.
Examples of PaaS
- Heroku
- Windows Azure
- Apache Stratos
- OpenShift
- AWS Elastic Beanstalk
- Heroku
- Google App Engine
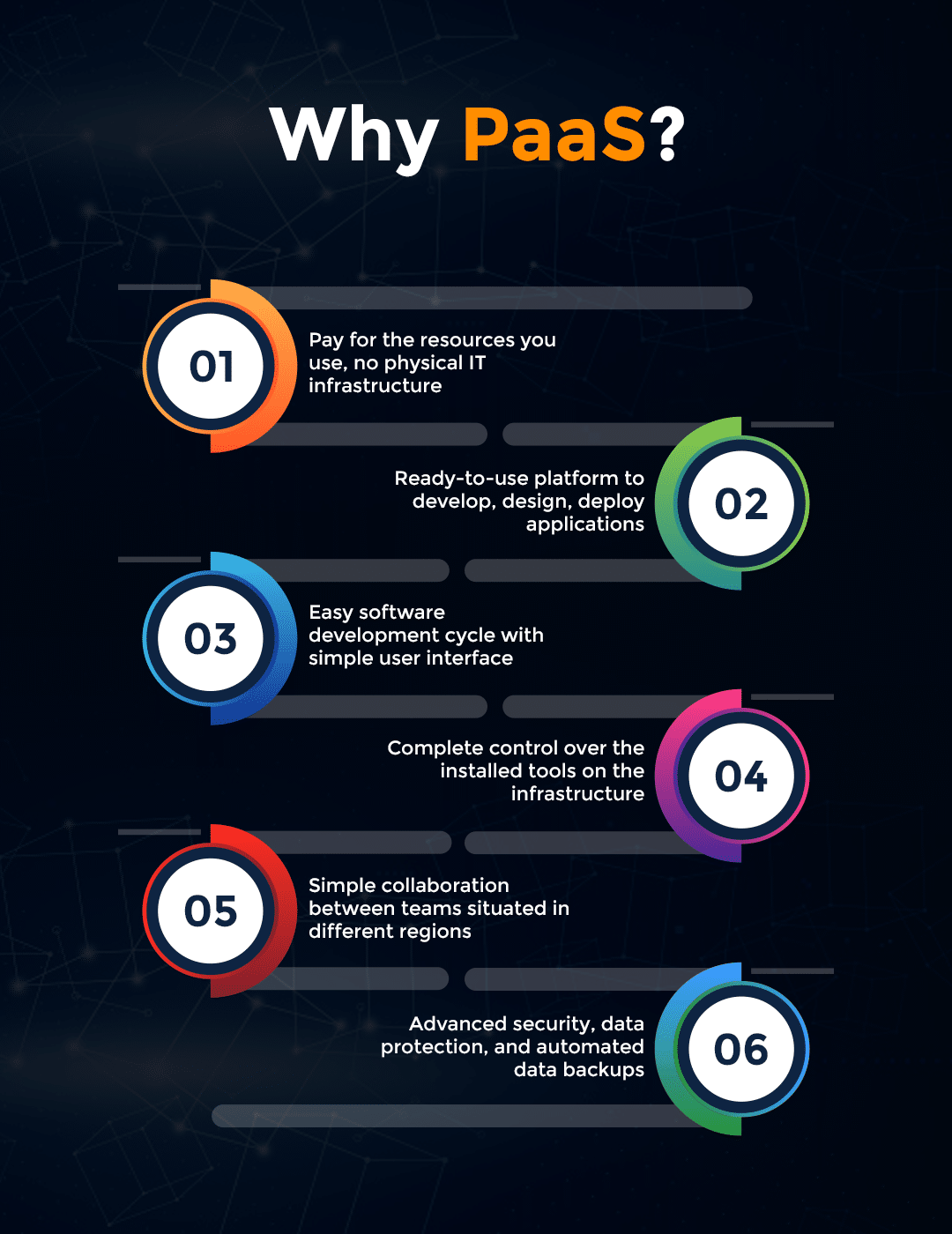
Main Benefits of Using PaaS
- Ease of use: Seamless software development, deployment, testing
- Code Easily: Developers can build advanced applications easily with less code
- Maintenance: Superfast innovation and no need to spend time to maintain core stack
- No Investment on Hardware: No need to purchase hardware or software to develop applications
- Simple UI: Completely web-based interface and multi-tenant architecture
Challenges of PaaS
- Fewer Permissions: No control over the infrastructure, everything is dependent on the vendor’s uptime
- Compatibility Issue: If the applications will not support some sort of development platform
- Risky: High risk of platform security and the user is responsible for the developed applications
3. SaaS (Software as a Service)
As the name indicates, SaaS is famous for delivering cloud-based applications and software to use over the Internet and it is also known as Cloud server Application Services. In this cloud service, the application is hosted online and individuals can use these applications by purchasing a subscription plan. All the applications offered by the SaaS cloud platform can be accessed simply through a browser or software through any device from all around the world.
The SaaS platform allows for the development, maintenance, test, and even updating the applications. Users can simply access the SaaS platform just by logging in and staying online as long as the applications are required to use. While using the SaaS platform, one does not need to install any software on the local system as everything is situated on the web.
Today everything is in the cloud and we all use SaaS products in our daily lives at some point. Cloud-based applications are mostly used by enterprises to easily develop, manage, monitor, and scale their business.
Examples of SaaS
- Google Workspace
- Dropbox
- Salesforce
- Google App Engine
- AWS Elastic Beanstalk
- Windows Azure
- OpenShift
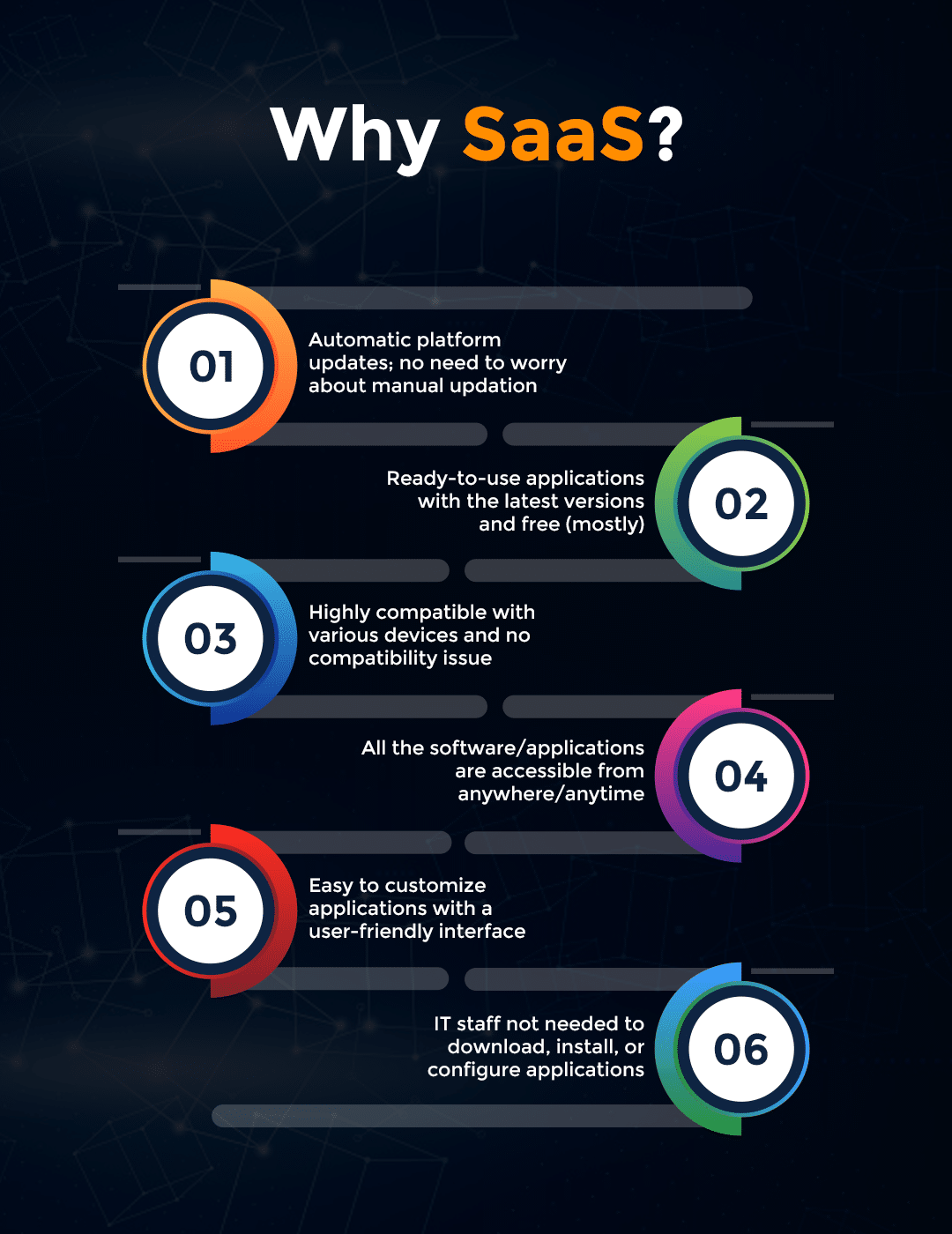
Main Benefits of Using SaaS
- Time-Saving: Saves a lot of time and money as IT team outsourcing is not required
- Focus on Quality: Developers are free to utilize their time on valuable business operations
- Automatic Updates: No need to worry about continuous upgrades and UX improvements
- Complete scalability: Integration with other platforms or applications
- Fewer Expenses: Free up-front licenses will result in reduced software usage expenses
Challenges of SaaS
- Security: Data security is in danger as all the sensitive information is saved within web apps
- Customization: Not many options to customize or add features to existing web applications/software
- Lock-in: Interoperability and vendor lock-in issue is one of the main concerns of SaaS platform
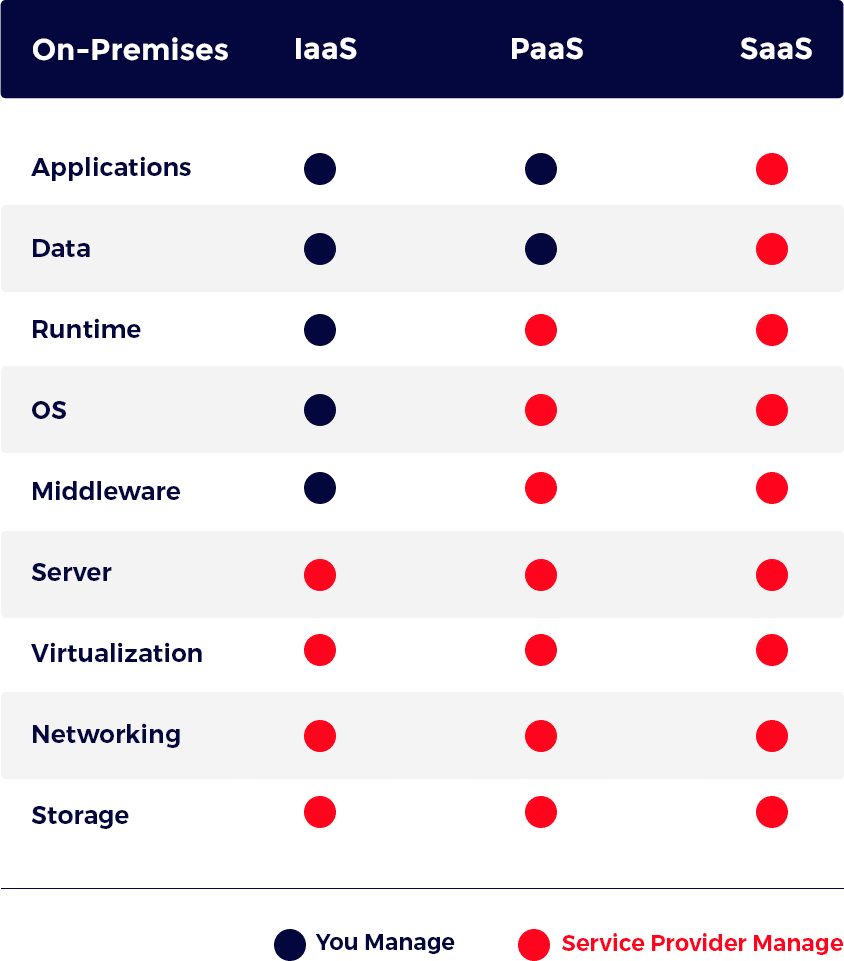
IaaS vs PaaS vs SaaS: The Key Differences
There’s So Much More Beyond IaaS vs PaaS vs SaaS Comparison
Well yes. Any service you can imagine physically can be in the cloud and here are some of the XaaS models of IaaS vs PaaS vs SaaS examples:
- Storage as a Service (STaaS)
- Containers as a Service (CaaS)
- Functions as a Service (FaaS)
- Hardware as a Service (HaaS)
- Database as a Service (DBaaS)
- Security as a Service (SECaaS)
- Disaster Recovery as a Service (DRaaS)
- Analytics as a Service (AaaS)
…and the list goes on.
IaaS vs PaaS vs SaaS: Which One Is The Best For My Business?
Now, you have all the details of each cloud service category and you can select the most appropriate services as per the capacity and requirements of your business. These services are a crucial component of cloud computing and their usage is increasing exponentially in our day-to-day lives. That’s why you should start using one (if not already) to automate most of your business processes.
Summarizing IaaS vs PaaS vs SaaS Comparison
The major difference between SaaS vs PaaS vs IaaS examples are the way of data management and maintenance:
- SaaS: No need for software or hardware, so you do not have to worry about data management or maintenance.
- IaaS: The user needs to manage all the resources to develop, host, build and run cloud services.
- PaaS: The user is allowed to manage the environment offered to build and deploy the applications, but not the server.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q 1. What is the difference between PaaS vs SaaS vs IaaS?
A. SaaS vs PaaS vs IaaS are the three main layers of cloud service delivery. Here SaaS stands for Software as a Service, PaaS – Platform as a Service, and IaaS – Infrastructure as a Service.
Q 2. Is AWS IaaS or PaaS or SaaS?
A. AWS (Amazon Web Services) is a combination of IaaS (Infrastructure as a service), and PaaS (Platform as a Service) and Packaged Software as a Service (SaaS).
Q 3. What is IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service)?
A. IaaS is a cloud computing solution that offers provisioning, managing, and computing service resources over the Internet, like servers, storage, devices, and virtualization devices.
Q 4. What is PaaS (Platform as a Service)?
A. PaaS is a popular cloud service model that offers a ready-to-use development environment for developers to stay focused on writing and implementing advanced code to create highly customized applications.
Q 5. What is SaaS (Software as a Service)?
A. As the name indicates, SaaS is famous for delivering cloud-based applications and software to use over the Internet and it is also known as Cloud Application Services.




