Difference Between SATA 2 vs SATA 3
IT Published on Date: February 19th 2025Storage technology has significantly evolved over the years, and one of the key advancements is the improvement of SATA (Serial ATA) interfaces. SATA is the standard interface utilized to connect storage devices like hard drives (HDDs) and solid-state drive (SSDs) to a computer’s motherboard.
Also, SATA has undergone multiple revisions, with SATA 2 (SATA II) and SATA 3 (SATA III) being two of the most widely utilized versions. In this article, we will explore the key differences between SATA 2 and SATA 3, including their compatibility, speeds, real-world applications, and performance.
As the formulation of SATA, the released mainstream SATA standard incorporates SATA I (also stated as SATA 1.0 or SATA 1.5 Gb/s), SATA II (also known as SATA 2.0 or SATA 3Gb/s) SATA III (also known as 3.0 or SATA 6Gb/s) and SATA express (also known as SATA 3.2 or SATAe). Let’s understand their particular speed.
Table of Content
SATA 1.0:5 Gb/s, 150 MB/s
SATA 2.0: 3 Gb/s, 300 MB/s
SATA 3.0: 6 Gb/s, 600 MB/s
SATAe: 16 Gbit/s, 1.97 GB/s
Understanding SATA 2
SATA 2 is the second generation of the SATA interface and was introduced as an improvement over SATA 1. Below are its key features:
Features of SATA 2
- Speed: 3 Gbps (300 MB/s)
- Backward Compatibility: Compatible with SATA 1 devices and cables
- NCQ (Native Command Queuing): Helps improve performance by optimizing read/write requests
- Hot Swapping: Allows devices to be connected and removed without shutting down the system.
- Improved Signal Integrity: Reduces errors in data transmission.
Limitations of SATA 2
While SATA 2 was a significant improvement over SATA 1, it had some limitations:
- Limited Speed: The 3 Gbps bandwidth can bottleneck modern high-speed SSDs.
- Lower Efficiency: Not as power efficient as SATA 3.
- Reduced Futureproofing: As storage technology evolved, SATA 2 quickly became outdated.
Understanding SATA 3
SATA 3 is the third generation of SATA and is the most largely used standard in modern computing. It provides several key improvements over SATA 2:
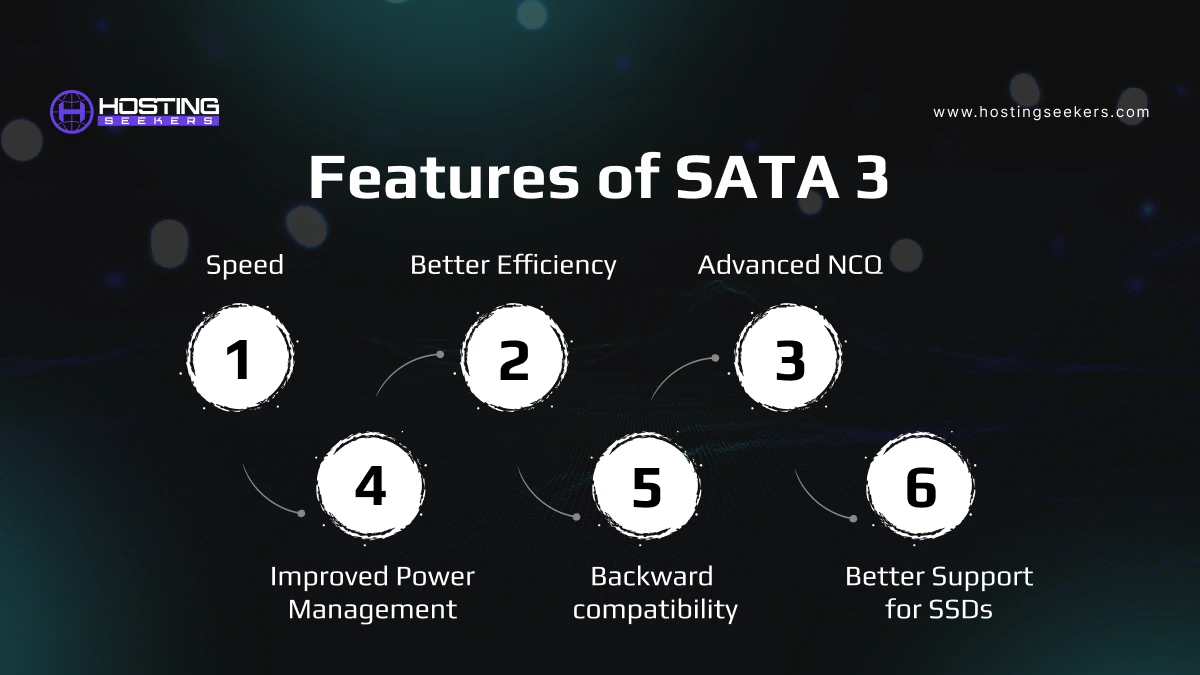
Features of SATA 3
Speed– It comes with 6 Gbps (600 MB/s), doubling the speed of SATA 2.
Better Efficiency – Improved Data transmission efficiency.
Advanced NCQ – Further optimizes data read/write operations.
Improved Power Management –Reduces power consumption in devices.
Backward compatibility– Works with SATA 2 and SATA 1 devices but at lower speeds.
Better Support for SSDs– Maximizes the performance of modern solid-state drives.
SATA 2 vs SATA 3: Comparison Table
| Feature | SATA 2 (SATA II) | SATA 3 (SATA III) |
| Speed | 3 Gbps (300 MB/s) | 6 Gbps (600 MB/s) |
| Backward Compatibility | Compatible with SATA 1 | Compatible with SATA 2 & SATA 1 |
| NCQ Support | Basic NCQ | Advanced NCQ |
| Power Efficiency | Moderate | Improved power management |
| Ideal For | HDDs and slower SSDs | High-speed SSDs and performance HDDs |
| Year Introduced | 2004 | 2009 |
| Maximum Theoretical Bandwidth | 300 MB/s | 600 MB/s |
| Cable Length Limit | 1 meter (3.3 feet) | 1 meter (3.3 feet) |
| Connector Type | Same as SATA 3 | Same as SATA 2 |
| Hot Plugging Support | Yes | Yes |
| Performance with SSDs | Bottlenecked | Optimized for SSDs |
| Error Correction Features | Basic | Improved error correction mechanisms |
| Data Burst Transfer Rate | Lower | Higher |
| Usage in Modern Systems | Limited | Standard |
Real-world Applications of SATA 2 and SATA 3
Home Users
For everyday users who primarily browse the web, stream videos, or perform basic computing tasks, SATA 2 may still be adequate, especially if using traditional HDDs. However, for those looking to speed up boot times and application loading, upgrading to a SATA 3 SSD is highly recommended as it provides significantly faster read and write speeds.
Gamers
SATA 3 SSDs drastically reduce game load times, leading to a smoother gaming experience. Games that require frequent asset loading, such as open-world titles, benefit greatly from the improved speed of SATA 3. Additionally, SATA 3 enhances overall system responsiveness, reducing stuttering and lag in resource-intensive gaming environments.
Content Creators
Graphic designers, video editors, and animators handle large media files that require high-speed storage. SATA 3 offers superior data transfer rates, enabling faster rendering, editing, and file transfers. This is particularly useful for 4K video editing and working with high-resolution images, as SATA 2 could cause slowdowns and longer processing times.
Enterprise & Servers
In professional environments where large databases, virtual machines, or RAID configurations are used, SATA 3 provides better performance and efficiency. The enhanced bandwidth and improved NCQ support allow for better multitasking and faster retrieval of data, which is crucial for businesses relying on large-scale storage solutions.
Laptop Users
SATA 3 improves battery efficiency in laptops by optimizing data transfer speeds and reducing power consumption. Laptops equipped with SATA 3 SSDs experience faster boot times, quicker file access, and overall improved system performance. This is especially beneficial for professionals who need portable yet high-performance machines for work on the go.
Summing Up
SATA 2 and SATA 3 represent different generations of the SATA interface, with SATA 3 offering double the speed and improved efficiency. While SATA 2 is still usable, it has limitations, especially for modern SSDs and high-performance applications. If you are using HDDs, the difference between SATA 2 and SATA 3 is minimal. However, if you want to maximize the performance of an SSD or high-speed storage device, SATA 3 is the best choice.
For those considering an upgrade, investing in a SATA 3-compatible motherboard or a PCIe adapter is a great way to future-proof your system and get the best storage performance possible. Understanding these differences will help you make an informed decision when selecting storage solutions for your computer setup.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) About SATA
1. Can I replace SATA 2 with SATA 3?
Yes, SATA 3 (6Gbps) is backward compatible with SATA 2 (3Gbps). You can replace a SATA 2 drive with a SATA 3 drive, but it will operate at SATA 2 speeds. Similarly, a SATA 3 motherboard port can support a SATA 2 drive, but again, at SATA 2 speeds.
2. How fast is SATA 2 vs. SATA 3?
- SATA 2: Has a maximum data transfer rate of 3 Gbps (300 MB/s).
- SATA 3: Has a maximum data transfer rate of 6 Gbps (600 MB/s).
However, real-world speeds depend on the drive’s performance, and SSDs will benefit the most from SATA 3.
3. Can I replace SATA 2 with SATA 3?
Yes, you can. SATA 3 is backward compatible with SATA 2, but the speed will be limited to SATA 2’s maximum bandwidth.
4. Does SATA 3 need a special cable?
Not necessarily. While SATA 3 cables are optimized for higher speeds, most standard SATA cables work fine for SATA 3. However, using a high-quality SATA 3-certified cable is recommended for optimal performance, especially with SSDs.
5. Does SATA 2 support SSD?
Yes, SATA 2 supports SSDs, but at a lower speed compared to SATA 3. Even with SATA 2, an SSD is still much faster than an HDD in terms of boot time and file access.
6. Where is SATA used?
SATA is used in desktop PCs, laptops, gaming consoles, external storage devices, and servers to connect hard drives (HDDs), solid-state drives (SSDs), and optical drives (DVD/Blu-ray).
7. Why is SATA used?
SATA is used because it provides a reliable, cost-effective, and widely compatible way to connect storage devices to computers. It supports hot swapping, offers decent speeds, and is easy to install and use.