How to Establish the Best Cloud Server for Small Businesses?
Cloud Industry Published on Date: March 27th 2024Cloud computing is now more than just a tool for small business but instead, it’s a demand for a business. Cloud servers offer many benefits over traditional on-premises servers that includes scalability, and lower upfront investment.
This guide will help you to establish the best cloud server for your small business. Let’s dive in.
Table of Content
What is a Cloud Server?
A Cloud server is a virtual server that runs in the cloud rather than as a physical machine on your business premises. The server is hosted by a cloud services provider in their data center. You can manage and access the server remotely over the network.
The cloud service providers takes care of organizing the physical hardware, so you can avoid capital expenditure on equipment. You pay only for the computing resources you actually utilize. This makes cloud servers ideal for small businesses with fluctuating resource needs.
There are a few types of cloud servers to choose from:
Small businesses can select from the several types of cloud servers for small business. Three main types are;
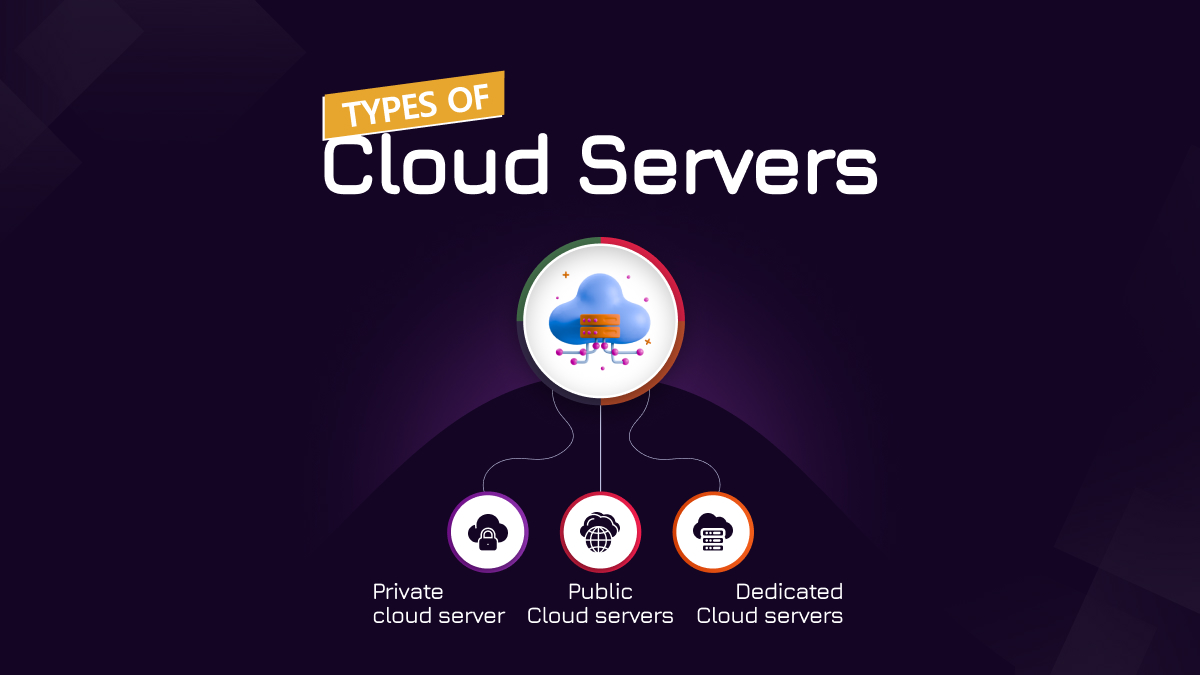
Private cloud server
A cloud server can also be a computer instance within an on-premises private cloud. In this case, an enterprise delivers the cloud server to internal users across LAN (Local Area Network) and, in some cases, also to external users across the internet.
Cloud-based Private servers for small businesses can rely on prefabricated instances but also allow users to select a desired amount of vCPU and memory resources to power the instance. Therefore, Hybrid clouds can include private or public cloud servers.
Public Cloud servers
The most common expression of a cloud server is a virtual machine or compute instance- that a public cloud provider hosts on its own infrastructure and delivers to users across the internet using a web-based interface or console.
Public cloud server mostly uses prefabricated instances, which assign a known number of virtual CPU and memory. Examples of cloud servers include Microsoft Azure, Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2) and Google Compute Engine instances.
Dedicated Cloud servers
In addition to virtual cloud servers, cloud providers can supply physical cloud servers named as a bare-metal servers which are dedicated cloud providers’ physical servers to a user.
These dedicated cloud servers also called dedicated instances, which are typically utilized when an organization must deploy a custom virtualization layer or mitigate the performance and security. Let’s check out the key features of cloud server
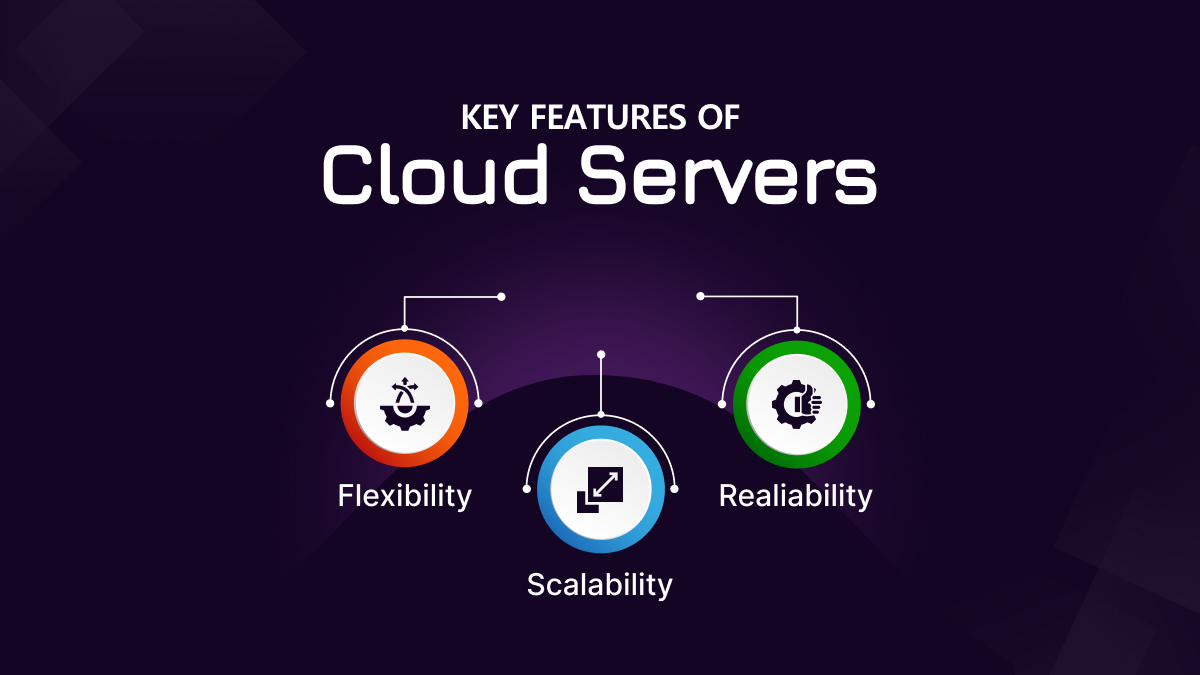
Key Features of Cloud servers
Cloud servers are virtual servers that run on cloud computing platforms. They are configured, created, and managed using software tools, and are accessed over the internet.
1. Flexibility
Cloud servers can be personalized and configured to meet the specific requirements for different applications and users.
2. Scalability
Cloud servers can be easily scaled up or down to meet changing demands, allowing organizations to pay only for the resources they need.
3. Reliability
Cloud providers typically offer high levels of uptime and reliability as well as backup and cloud disaster recovery solutions.
How to choose a Cloud server for small business?
When choosing a cloud server for a small business, there are a few key factors that you need to consider:
Cost
Compare the pricing of different cloud servers to ensure that it is cost-effective and is the best value for money.
Features
Look for a cloud server that provides the features you need like reliability, scalability, and security.
Reputation
Take into consideration the identity of the cloud provider, and also read reviews from other users to get a sense of their experience.
Steps to set up the best cloud services for small business
Once you have selected your cloud provider, it’s time to set up a cloud server hosting for your small business. This process typically involves the following steps:
1. Select server configuration
The first step is deciding on the right server configuration for your needs. So, consider various factors like the Number of CPU cores as more crores allows for faster processing and multi-threading. Another vital factor in setting up a cloud server is to set up RAM capacity, you can aim for at least 8GB for most business uses. Go high you are 3aiming to run large databases.
While making configuration choices, try to balance cost and performance. The good thing is that cloud servers make it easy to change these settings later when required. As an example, for a web server, a 2 GHZ CPU with 2 GB RAM and 500GB storage is good to start.
2. Select the server Location
Your server location is another vital thing to consider when setting up your location for your server, always pick the region near to you and your user base for the fastest clients or business. Check that the provider has redundant servers in that location to guarantee high availability.
In addition, selecting the optimal server location is something that can significantly improve application or website performance. So make sure you have made the best choice available.
3. Select an operating system
For the OS, the main options are Linux-based or Windows. Linux is open-source and cost-effective.
With the options like CentOS, Ubuntu, Debian, etc. Windows server OS comes with licensing fees but offers a user-friendly GUI and compatibility with .NET applications. You should select the OS that best aligns with your applications stack and Admin experience.
4. Review Security Provisions
Take time to investigate and monitor the available security options in order to find ones that meet your compliance and risk tolerance requirements. You can always look for robust features like an application firewall (WAF) to filter malicious HTTP requests.
Also, DDoS mitigation to protect against volumetric attacks. Also, private network options are away from the public internet.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q 1. What is a cloud server, and why should my small business consider using one?
Ans. A cloud server is a virtual server that runs in a cloud computing environment. It offers scalability, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness compared to traditional on-premises servers. The best cloud server list for small businesses benefits from the ability to scale resources as needed, pay only for what they use, and access their data and applications from anywhere with an internet connection.
Q 2. What factors should I consider when choosing a cloud server provider for my small business?
Ans. Factors to consider include reliability, security features, scalability, pricing structure, customer support, integration capabilities with existing systems, and compliance with industry regulations.
Q 3. How much storage and computing power do I need for my small business’s cloud server?
Ans. The amount of storage and computing power you need depends on factors such as the size of your business, the volume of data you generate and process, the number of users accessing the server, and the type of applications you run. Start by estimating your current needs and consider scalability for future growth.
Q 4. What security measures should I implement to protect my small business’s data on a cloud server?
Ans. Security measures include data encryption, multi-factor authentication, regular backups, access controls, monitoring and logging, and compliance with industry security standards such as HIPAA or GDPR, if applicable to your business.
Q 5. How can I ensure that my small business’s cloud server is always available and responsive?
Ans. Choose a reputable cloud server provider with a proven track record of reliability and uptime. Implement redundancy and failover mechanisms to minimize downtime, and regularly monitor server performance to identify and address any issues promptly.
Q 6. How do I migrate my small business’s data and applications to a cloud server?
Ans. The migration process involves assessing your current infrastructure, selecting the appropriate cloud services and tools, preparing your data for migration, testing the migration process, and finally executing the migration with minimal disruption to your business operations.