What is a Subdomain and When to Use One?
Domains Published on Date: January 22nd 2025Website or online stores play a crucial role in enhancing businesses. The key aspect of website architecture is understanding about the various domain structures. This blog will help you into understanding the concept of subdomains, while explaining what a subdomain is, their structure, and when to effectively utilize them for increasing your online presence and how they benefit your business.
Table of Content
What is a Subdomain?
A Subdomain is the add on or a prefix added to your main domain name to separate a section of your website. In other words, a subdomain is mainly the division of main domain. It’s like creating a separate section or category within your primary website, each with its own unique address.
What is the Structure of Subdomain?
A URL with a subdomain is made up of three parts:
Subdomain: The prefix used in the domain name.
Primary domain: The core part of the domain name.
TLD: The suffix or top-level domain.
For example, blog.example.com; in which “blog” is the subdomain, “example” is the primary domain and “.com” is the top-level domain.
How to Create a Subdomain?
Creating a subdomain is not a typical task. To create a subdomain, one should follow these simple steps:
Step 1: Log in to your cPanel
Log in into your control panel of your domain registrar or Domain hosting provider.
Step 2: Locate DNS management
Look for a section related to “DNS,” “Name Servers,” “Zone Editor,” or something similar.
Step 3: Create a new record
Click on “Add Record,” “New Record,” or a similar button.
Step 4: Choose the record type
There will be two options:
– A Record: Use this for subdomains that point to an IP address. It is most (commonly) used option.
– CNAME Record: Use this for subdomains that point to another domain.
Step 5: Fill the necessary details
1. Host (or Name): Enter the desired subdomain name (e.g., “blog” for “blog.example.com”).
2. Value:
– For A Record: Enter the IP address of the server where the subdomain’s content will be filled.
– For CNAME Record: Enter the full domain name of the target website.
3. TTL (Time to Live): This determines how long DNS records are cached by internet service providers.
Leave it at the default value unless you have specific needs.
Step 6: Save and Apply
Click on the “Save” and “Apply” button to finalize the changes made.
Step 7: Wait for propagation
It can take some time, generally a few minutes or a few hours, for the DNS changes to propagate across the internet.
Choosing the best domain registration provider is crucial for building a strong brand identity, to ensure credibility, and to foster customer loyalty over time. To enhance your online presence and build lasting customer relationships, consider utilizing premium domain name registration services. Search for best domain hosting providers on HostingSeekers.
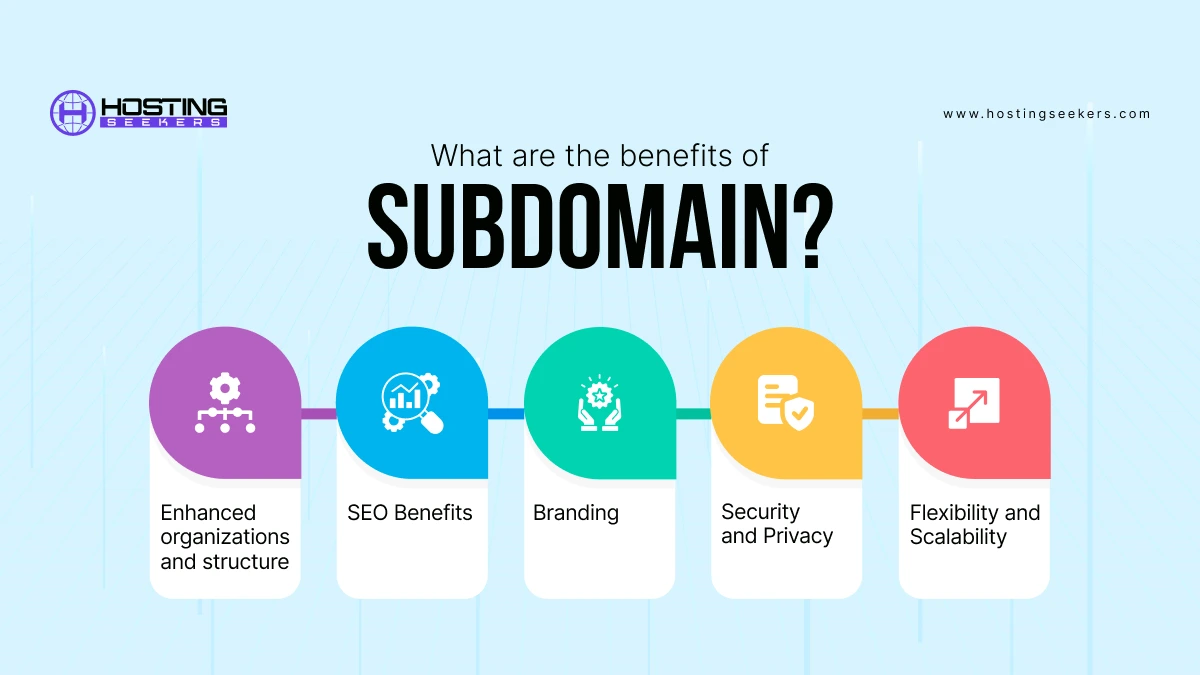
What are the Benefits of Subdomain?
The benefits of subdomain are:
1. Enhanced Organizations and Structure
Subdomains allow you to logically and technically organize all the sections of your website under different names to navigate easily.
This helps to improve user experience by making it easier for visitors to find the information they’re looking for. By creating separate subdomains for specific purposes (e.g., a blog, store, or support area), you can establish a clear structure within your website’s architecture.
2. SEO Benefits
Search engines often treat subdomains as separate pages. This can lead to improved search engine rankings for specific subdomains, especially if they target particular keywords or audiences.
Subdomains can help you target specific keywords more effectively. For example, a “blog” subdomain can be optimized for relevant blog-related keywords.
3. Branding
Subdomains help you create distinct or different branding identity for various sections of websites. This can be useful for businesses to streamline multiple brands and products seamlessly.
By using subdomains consistently, you can enhance your brand identity and make it more reliable for visitors.
4. Security and Privacy
Subdomains can be used to separate sensitive areas of your website, such as customer login portals or administrative areas. It provides an extra layer of security.
By separating different sections of your website into subdomains, you can better control access and privacy settings for each section.
5. Flexibility and Scalability
Subdomains provide a flexible way to expand your website’s functionality without major restructuring. You can easily add new subdomains as per your needs.
Subdomains can simplify website management by allowing you to manage different sections independently.
Other Benefits:
Experimentation: Subdomains can be used to test different website designs, features, or marketing strategies without affecting the main website.
Geo-targeting: Subdomains can be used to target specific geographic regions or language groups with localized content.
Hosting reseller: Subdomains can be used to provide dedicated hosting spaces for clients or partners.
Cost effective: Subdomains are cost effective. As per your web hosting plan, once you have bought a domain you can add subdomains for no cost.
What is the Difference Between Subdomain and Domain?
Factors |
Subdomain |
Domain |
| Definition | A Subdomain is the add on or a prefix added to your main domain name to separate a section of your website. | A domain is the principal web address or in other words main address of the website. |
| Structure | A Prefix added to the main domain. | Consists of Second-Level Domain (SLD) and a Top-Level Domain (TLD). |
| Example | blog.example.com | example.com |
| Ownership | Subdomains are extensions of the main domain. | You own the domain, which requires registration with a domain registrar. |
| Relation | Represents the address of a subsection of the website. | Represents the primary address of the website. |
| Purpose | Used to extend website address. | Used to create a brand. |
| Use Cases | Organizing large websites, managing separate projects, or creating specific branding. | Creating primary website address or brand identity. |
| Best for | Best for niche targeting. | Best for creating unified brand experience. |
| Independence | Part of a larger domain and relies on the main domain. | Independent entity with its own identity. |
| SEO Impact | Lesser impact on main domain’s SEO. | Significant impact on SEO. |
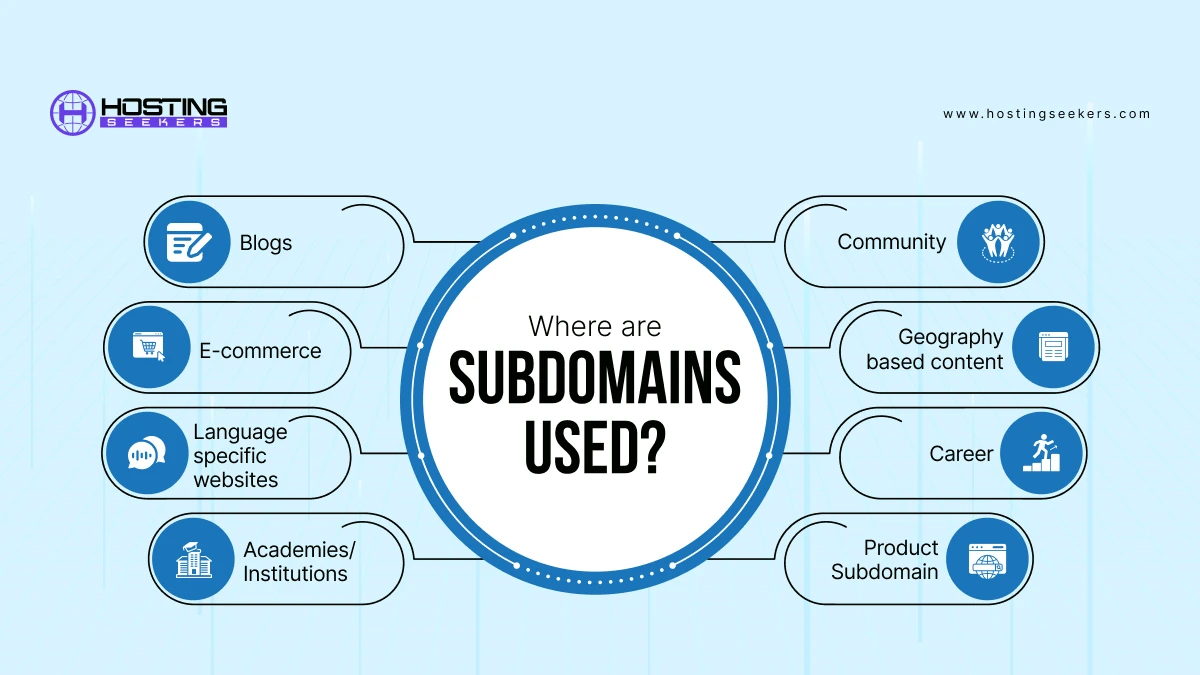
Where are Subdomains Used?
Subdomains are used in:
1. Blogs: This is a classic use case. It separates blog content from the main website, allowing for a distinct look and feel, easier navigation, and improved SEO for blog-specific keywords. For example: Blog.exaple.com.
2. E-commerce: This isolates the online store from the main website, providing a dedicated space for product browsing, shopping cart functionality, and order processing. For example: Shop.example.com.
3. Language specific websites: This allows businesses to cater to different language markets with localized content, improving user experience and accessibility for international audiences. For example: German.example.com.
4. Academies/Institutions: This helps organize internal resources and information for different groups within an institution, such as students, faculty, and staff. For example: Students.university.edu, result.university.edu, Alumni.university.edu.
5. Community: This creates a dedicated space for online communities, forums, or social interaction related to the main website’s topic. For example: community.example.com, forum.example.com.
6. Geography based content: This allows businesses to target specific geographic regions with localized content, promotions, and pricing. For example: uk.example.com (United Kingdom), us.example.com (United States).
7. Career: This creates a dedicated section for job postings, applicant tracking system, and other career-related information, streamlining the recruitment process. For example: careers.example.com.
8. Product subdomain: This creates a separate section for all the products in respective to their size, pattern, fabric, type, etc. For example: Shirts.example.com, jeans.example.com.
When Should One Use Subdomains?
Use subdomains when:
1. You need a separate theme with independent content management.
2. Need to host multiple projects or websites under the same main domain umbrella.
3. Targeting specific audience; based on language, geography and more.
4. Require different SEO strategies for various sections.
5. For hosting development or testing environments for your website without affecting the live site.
Conclusion
A subdomain is a valuable tool that allows site owners to organize a website and enhance their users’ experiences. It makes it easy for the users to navigate the website. Not only that, but it can be a tool for improving your Search Engine Optimization (SEO). Search Engine Optimization is the set of practices used to enhance the organic visibility of your website or web page on internet within a search engine’s search results page (SERP). As you can see, the subdomain can be used to improve search engine optimization (SEO). All these benefits can help you reach your online goals.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. What is the difference between Subdomain and Subdirectory?
Ans. A subdomain is the separate address from your main domain or a subsection of your main website while a subdirectory is a folder within your main domain.
Q2. How does subdomain effect SEO?
Ans. Subdomains can have a separate SEO identity, but their impact on the main domain’s SEO can be less.
Q 3. Where are subdomains used?
Ans. Subdomains are used for blogs, e-commerce stores, language-specific versions, separate projects, and many more.
Q 4. Is it difficult to create a subdomain?
Ans. Creating a subdomain is usually a simple process that can be fulfilled through your domain registrar or hosting control panel.
Q 5. What is the structure of Subdomain?
Ans. Structure: Subdomain, Primary domain, TLD (top level domain). For example, blog.example.com; in which “blog” is the subdomain, “example” is the primary domain and “.com” is the top-level domain.