What is DNS Lookup? Common Tools and Commands for DNS Lookup
Domains Updated on : August 14, 2025The smooth operation of websites and internet services is supported by a number of enabling technologies. The Domain Name System (DNS) is one of the most essential of these technologies. DNS essentially converts human-readable domain names such as “example.com” into IP addresses that computers understand so as to find each other on the network. How does the conversion take place? And which instruments can you use in order to investigate the complexities surrounding DNS? In this article, we will delve into What DNS lookup means, also some best DNS lookup tools and commands for making a DNS query.
Table of Content
What is DNS Lookup?
DNS lookup is the process in which a device or computer requests info from an Internet management system (DNS server) to find the numeric IP address linked to a domain name.
For instance, when you enter a website name, DNS lookup translates that name into the corresponding IP address. This is how your computer knows where to fetch the data from and load the website you want to visit. It is often assumed that DNS lookup and reverse DNS lookup are the same, which leads to confusion. So, let’s understand both:
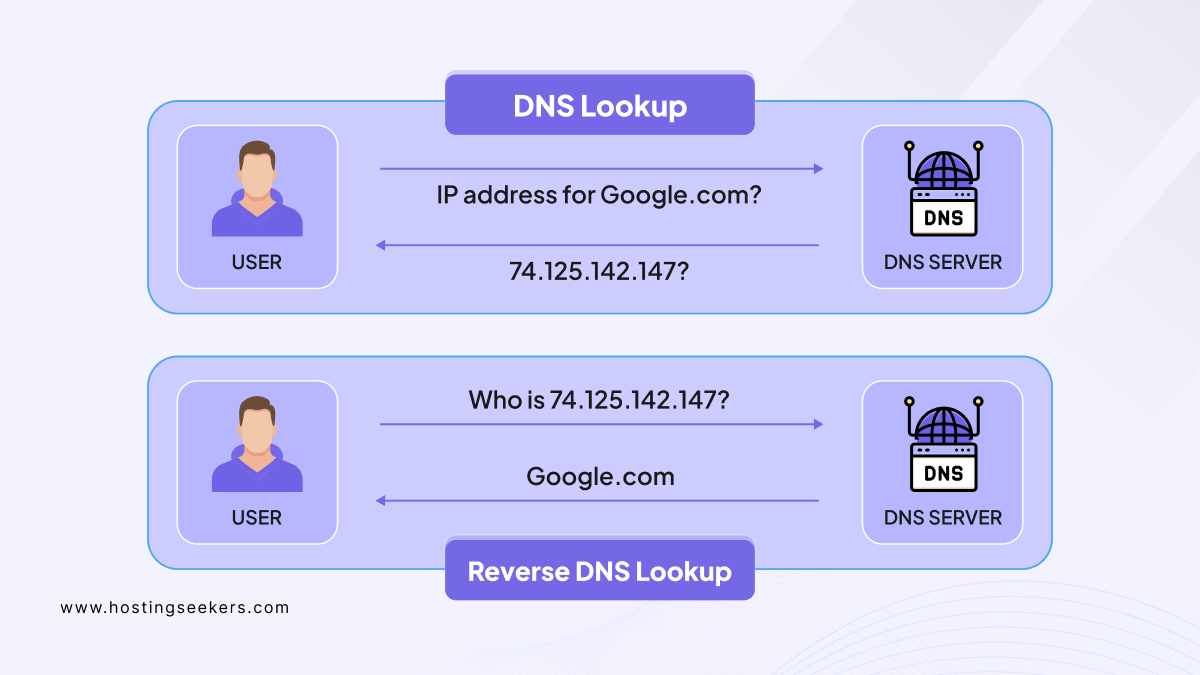
DNS Lookup |
Reverse DNS lookup |
| Translates domain names into IP addresses. | Translates IP addresses into domain names. |
| Offer information about DNS records. | Give information about domain reputation and ownership. |
| Offers details like AAAA, A, CNAME, MX, NS, PTR, SRV, TXT, and SOA records. | Offer PTR records mapping IP addresses to domain names. |
| Help to solve domain names to build and develop connections. | Helps to identify the domain associated with an IP address. |
| It is utilized for verifying DNS configurations and troubleshooting DNS related issues. | It is utilized for verifying the legitimacy of email senders and identifying potential security threats. |
How Does DNS Lookup Work?
The DNS lookup process is a sequence of steps to retrieve the IP address that collaborates with a domain name. This process includes querying multiple DNS servers, starting with a recursive lookup at the DNS resolver, shifting to the root server, then to the TLD (Top Level Domain) server, and finally, to the authoritative name server, which holds the actual IP address of the domain.
This process is more important to drive traffic and network maintenance on the internet, allowing users to access websites efficiently utilizing familiar domain names.
The Best Command-Line DNS Lookup Tools
Command-line DNS lookup tools are indispensable for IT professionals, network administrators, and anyone involved in troubleshooting or managing network infrastructure. Let’s check out the vital essential command-line DNS lookup tools:
1. Dig
Dig provides detailed information on different DNS records like MX, AAAA, A, NS, etc.) with the ability to perform interactive queries. Also, it is best for diagnosing DNS issues and in-depth analysis.
Usage: dig @nameserver domainname recordtype”
Example output:
; <<>> DiG 9.16.1-Ubuntu <<>> example.com
;; ANSWER SECTION:
example.com. 86400 IN A 93.184.216.34
;; Query time: 42 msec
;; SERVER: 8.8.8.8#53(8.8.8.8)
2. nslookup
It is user-friendly and suitable for immediate IP lookups or MX record checks. It is available on most operating systems, including Windows, macOS, and Linux.
Usage: nslookup domainname` or `nslookup -query=recordtype domainname
Example output:
Server: dns.google
Address: 8.8.8.8
Non-authoritative answer:
Name: example.com
Address: 93.184.216.34
3. host
Known for being user-friendly, it streamlines DNS lookups by translating domain names to IP addresses and vice versa.
Usage: hostname` or `host -t recordtype domainname
Example output:
example.com has address 93.184.216.34
Web-Based DNS Lookup Tools
Web based DNS lookup tools provide a user-friendly interface for performing DNS zone related issues directly from your browser. Let’s check out some popular web-based DNS lookup tools.
1. intoDNS
intoDNS monitors the health and configuration of DNS and mail servers, offering a comprehensive report that covers different factors like MX records, NS records, and potential errors with domain setup. Let’s understand the pros and cons of intoDNS:
Pros
- MX records, NS records, and possible misconfigurations are just a few of the topics covered in-depth DNS health and configuration reports that are provided by intoDNS.
- The program is commended for having an intuitive UI that is simple to use and accessible to people of all technical backgrounds.
- Since intoDNS provides its essential services without charge, it is a desirable choice for people and small companies wishing to verify the DNS for their domains without having to make a commitment.
Cons
- While DNS provides comprehensive reports, some users feel that the depth of analysis can only be restricted if you opt for robust features.
- intoDNS offers a snapshot of DNS configuration at a specific time, but it does not provide real-time monitoring or alerts for DNS changes.
- As its popular due to its free access, intoDNS server can sometime become overloaded, leading to slow response times or temporary unavailability.
2. MxToolbox
Mxtoolbox is more versatile that specialized in checking MX (Mail exchange) records and performing blocklists, SMTP diagnostics, and more, make it more top choice for email server troubleshooting.
Pros
- MxToolox provides a wide range of tools for blacklist checks, DNS investigation and email deliverability analysis.
- Also, one of the robust features of Mxtoolsbox is its real-time tracking service, which alerts users if their domain or IP is listed on a blacklist.
- Users appreciate the clean and intuitive interface of MxToolbox, which simplifies the process of analyzing and conducting tough DNS and email deliverability checks.
Cons
- As MxToolbox provides a free tier, by giving the whole access to the full range of tools and features, incorporating comprehensive alerting and monitoring services that need a paid subscription.
- Also, some users find that while the basic functions of MxToolnox are straightforward, it enables most of its advanced analytics and features needing a steeper learning curve.
- Also, some of the users have reported that the alert system, mainly for blacklist monitoring can sometimes be overly sensitive, leading to notification that may not always signify an urgent or significant issue.
3. DNSInspect
With its free web-based service, DNSInspect analyzes and tracks mail server and DNS setups and provides thorough information on the functionality and state of your DNS infrastructure.
Pros
- With DNSInspect, you can examine DNS settings in detail and have frequent problems with NS, MX, SOA records, and other records checked out.
- Users praise DNSInspect’s simplicity, pointing out that it’s easy to do DNS checks without requiring complex technical expertise thanks to its user-friendly interface.
- The fact that DNSInspect offers its services without charge is one of the main benefits that customers have emphasized. This makes it a great resource for individuals, small businesses, or anybody else wishing to perform a fast DNS health check without having to pay for anything.
Cons
- Despite receiving accolades for its free service, some users point out that DNSInspect lacks some of the more sophisticated features and in-depth analytical capabilities of more expensive DNS solutions.
- Owing to its free model, DNSInspect occasionally experiences large traffic volumes, which can cause sporadic timeouts or slower response times during periods of strong usage.
- While DNSInspect’s capability is mainly restricted to one-time inspections, it does provide continuous monitoring and real-time notifications for DNS changes or faults, unlike some other DNS tools.
Summing Up
Mastering DNS management and domain troubleshooting is vital for anyone responsible for overseeing network infrastructure. Each tool comes with unique features tailored to different factors of DNS management, so whether you are conducting detailed domain analyses or monitoring DNS propagation worldwide.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q 1. What is the DNS lookup tool?
Ans. The DNS lookup tool is a utility that allows users to retrieve information about domain names from the Domain Name System (DNS). It helps in finding the IP address associated with a domain name, verifying DNS records, and troubleshooting DNS-related issues.
Q 2. What is the DNS lookup command?
Ans. The DNS lookup command, commonly known as nslookup, is a command-line tool used to query DNS servers and obtain domain name information such as IP addresses, MX records, and other DNS-related details. It is available on most operating systems.
Q 3. What are the steps in a DNS lookup?
Ans. The DNS lookup process involves the following steps: See the How DNS Lookup Works (Step-by-Step) section for the complete explanation.
- Query Initiation: The user enters a domain name in a web browser or a command-line tool.
- Recursive Query: The local DNS resolver sends a request to a DNS server.
- Root Server Contact: The DNS server queries a root server if it doesn’t have the necessary information.
- TLD Server Contact: The root server directs the query to the appropriate Top-Level Domain (TLD) server.
- Authoritative DNS Server: The TLD server directs the query to the authoritative DNS server for the domain.
- Response: The authoritative DNS server responds with the IP address or other DNS records.
Q 4. How many DNS lookups are there?
Ans. There are two main types: Forward DNS Lookup and Reverse DNS Lookup.
| Type | Description | Common Uses |
|---|---|---|
| Forward DNS Lookup | Converts a domain name into its corresponding IP address. This is the standard process used when visiting websites. | Web browsing, application connections, and verifying DNS records |
| Reverse DNS Lookup | Converts an IP address into its associated domain name. This is essentially the opposite of forward lookup. | Email server verification, security checks, and network troubleshooting |
Q 5. Why use DNS lookup?
Ans. DNS lookup is essential for resolving domain names to IP addresses, which is necessary for web browsing, email routing, and other internet services. It helps in troubleshooting connectivity issues, verifying domain ownership, and ensuring the proper functioning of DNS records.
Q 6. How to use the nslookup tool?
Ans. To use the nslookup tool, follow these steps:
- Open a command prompt or terminal on your computer.
- Type nslookup followed by the domain name you want to query (e.g., nslookup example.com).
- Press Enter to execute the command.
- Review the output, which will display the IP address associated with the domain, along with other relevant DNS information.




