Multi-Cloud vs. Hybrid Cloud: What’s the Difference?
Cloud Industry Comparison Published on Date: July 30th 2024Today’s businesses seek the best combination of cloud solutions to meet their requirements. Deployments using multiple clouds and hybrid clouds achieve this. Whereas multi-cloud uses services from several cloud providers, hybrid cloud combines cloud services with on-premises infrastructure. Multi-cloud emphasizes using many providers’ offers at the same time for different business purposes, whereas hybrid focuses on mixing.
To simplify things, consider hybrid clouds combining apples and oranges, whereas multi-clouds combine several kinds of apples. To enhance your comprehension and make informed decisions regarding the best option for your company, let’s delve into the specifics of cloud computing and see how these methods might benefit your operations.
Table of Content
What is Multi-Cloud?
Multi-cloud computing means distributing cloud-based resources, applications, and software across numerous environments. Because different cloud services use a mix-and-match approach, multi-cloud architecture is kept current, especially for a particular application. The flexibility to employ two or more private clouds or cloud services rather than depending solely on one is the primary benefit of a multi-cloud model for many enterprises. However, multi-cloud prevents these many services from being linked together.
Benefits of Multi cloud
1. Avoidance of Vendor Lock-In
By using services from multiple cloud providers, organizations can avoid dependency on a single vendor. This provides flexibility to switch providers, if necessary, without being tied to one particular ecosystem.
2. Improved Reliability and Redundancy
Utilizing multiple cloud providers can enhance system reliability and availability. If one cloud provider experiences an outage, services can continue to run on another provider, ensuring business continuity.
3. Optimized Performance
Different cloud providers excel in different areas. By leveraging the strengths of each provider, organizations can optimize performance for various workloads. For example, one provider might offer better data analytics tools, while another provides superior storage solutions.
4. Cost Efficiency
Multi-cloud strategies can help organizations optimize costs by taking advantage of the most cost-effective services and pricing models offered by different providers. Organizations can choose the best-priced services for their specific needs.
5. Enhanced Security and Compliance
Spreading workloads across multiple cloud providers can improve security by reducing the risk associated with a single point of failure. Additionally, different cloud server providers might offer unique compliance certifications that collectively meet various regulatory requirements.
6. Scalability and Flexibility
A multi-cloud approach allows organizations to scale resources as needed across different providers, providing greater flexibility to handle varying workloads and demands.
What is Hybrid Cloud?
The term “hybrid cloud” describes a combination of third-party cloud services and on-premises private clouds. Apart from customary data centers, it is also referred to as a public or private cloud. In essence, it consists of different cloud arrangements. One public and one private cloud, or two private and one public cloud, could be combined.
In the business world, hybrid and multi-cloud clouds differ in numerous ways. It’s common to use both names interchangeably. Multi-cloud computing is becoming standard practice for many firms, so this differentiation is anticipated to increase.
Benefits of Hybrid Cloud
1. Flexibility and Scalability
Hybrid cloud allows organizations to scale resources as required. They can keep sensitive data on a private cloud and use the public cloud for non-sensitive, high-volume tasks to bring about flexibility and cost-efficiency.
2. Cost Efficiency
By running predictable and stable workloads on the private cloud, and variable workloads on the public cloud to take advantage of the pay-as-use model, organizations achieve cost optimization. This prevents overprovisioning and thus helps in reducing the costs of infrastructure.
3. Improved Security and Conformance
Sensitive data and critical applications can be maintained in a private cloud while moving less critical and less sensitive workloads to the public cloud. This will satisfy the regulatory and compliance requirements in the process and ensure the protection of data but still have the capability for public cloud scale.
Difference Between Multi-Cloud vs Hybrid Cloud
Multi-Cloud |
Hybrid Cloud |
| Involves making use of several cloud computing services from various cloud service providers. | Involves utilizing cloud-based and on-premises infrastructure in combination. |
| Increases cost-effectiveness, flexibility, and resilience by utilizing the distinct advantages of several cloud platforms. | Utilize scalability and flexibility of cloud computing while enabling increased control and protection over sensitive data. |
| Can offer access to a greater selection of services and lessen the chance of vendor lock-in. | May be more difficult to manage and present difficulties with interoperability and data integration. |
| Requires meticulous preparation and oversight to guarantee top performance and security across various cloud providers. s. | Can offer a compromise between the advantages of cloud computing and the requirement to have some degree of infrastructure control. |
How to Choose Which Cloud is Best for Your Business?
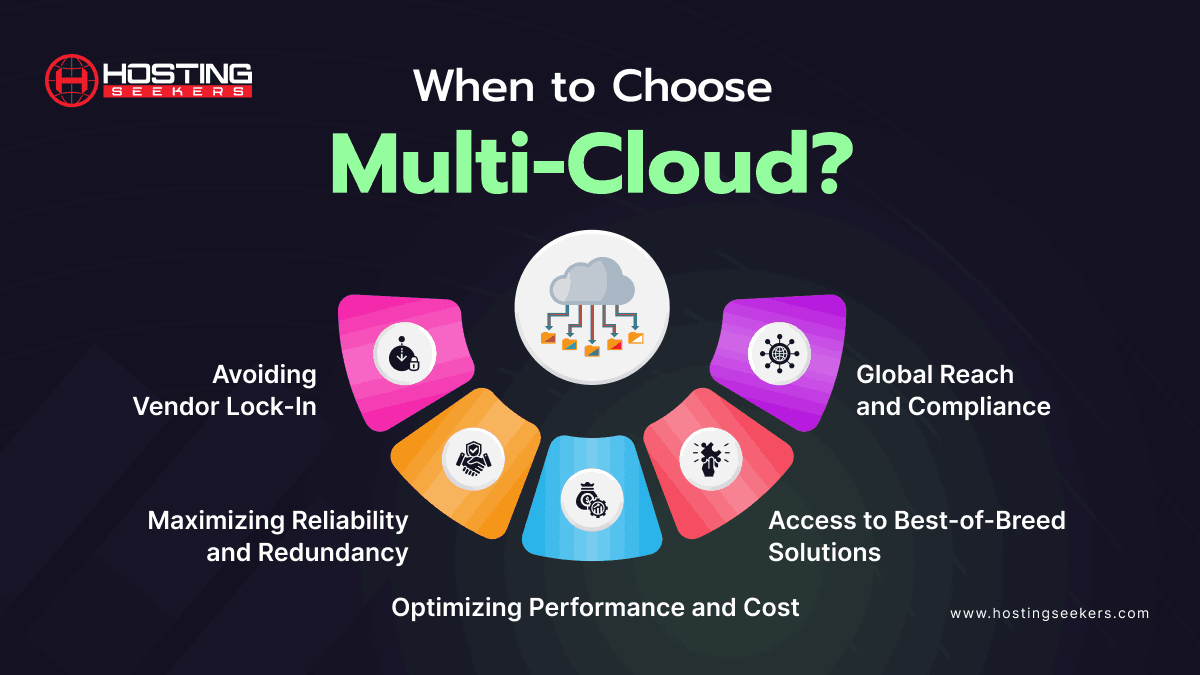
When to Choose Multi-Cloud?
A multi-cloud strategy involves using multiple cloud services from different providers. This approach is suitable when:
1. Avoiding Vendor Lock-In: You want to avoid dependency on a single cloud provider and ensure flexibility to switch vendors if needed.
2. Maximizing Reliability and Redundancy: You need to ensure high availability and disaster recovery by distributing workloads across multiple providers to mitigate the impact of potential outages.
3. Optimizing Performance and Cost: You aim to optimize performance by using the strengths of different providers for specific tasks and take advantage of cost savings by leveraging the most cost-effective services.
4. Access to Best-of-Breed Solutions: You want to utilize the best services available from different providers, such as superior analytics tools from one provider and advanced storage solutions from another.
5. Global Reach and Compliance: You need a global presence with data centers in multiple regions and require compliance with various regional regulations, which different providers may specialize in.
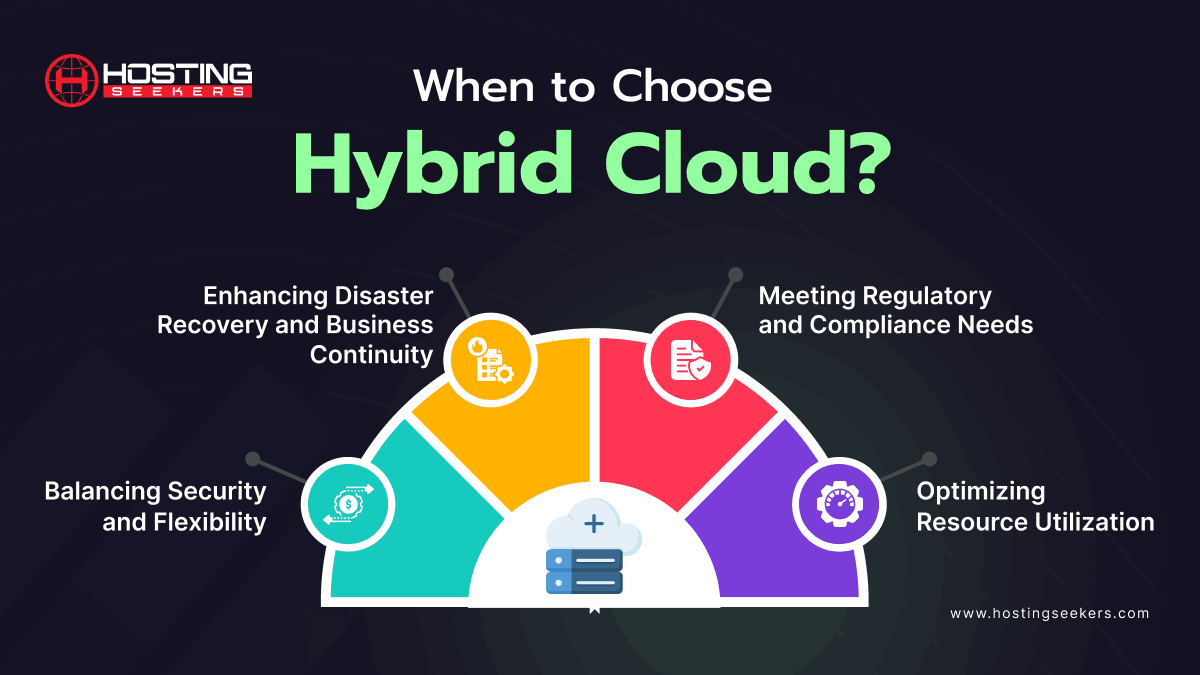
When to Choose Hybrid Cloud?
A hybrid cloud strategy combines private and public clouds, providing a blend of both environments. This approach is suitable when:
1. Balancing Security and Flexibility: You need to keep sensitive data secure on a private cloud while benefiting from the scalability and flexibility of the public cloud for less sensitive workloads.
2. Enhancing Disaster Recovery and Business Continuity: You require a robust disaster recovery plan, where critical data and applications can be maintained on a private cloud while using the public cloud for backup and failover.
3. Meeting Regulatory and Compliance Needs: You must comply with stringent regulatory requirements that mandate certain data to remain on-premises or within a private cloud, while still needing the public cloud’s capabilities.
4. Optimizing Resource Utilization: You want to optimize resource use by running stable workloads on a private cloud and utilizing the public cloud for peak loads or variable demands.
Summing Up
Different cloud deployment strategies, such as multi-cloud and hybrid cloud deployments, are appropriate for particular use cases. Both models provide efficient corporate services and facilitate easy access to cloud computing platforms. However, make sure to weigh the benefits and drawbacks of various cloud strategies when choosing a cloud deployment strategy for a task or moving data to a new cloud.